Breastfeeding for reducing the risk of pneumonia morbidity and mortality in children under two: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 24564728
- PMCID: PMC3847465
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2458-13-S3-S18
Breastfeeding for reducing the risk of pneumonia morbidity and mortality in children under two: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Suboptimal breastfeeding practices among infants and young children <24 months of age are associated with elevated risk of pneumonia morbidity and mortality. We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to quantify the protective effects of breastfeeding exposure against pneumonia incidence, prevalence, hospitalizations and mortality.
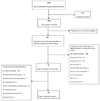
Methods: We conducted a systematic literature review of studies assessing the risk of selected pneumonia morbidity and mortality outcomes by varying levels of breastfeeding exposure among infants and young children <24 months of age. We used random effects meta-analyses to generate pooled effect estimates by outcome, age and exposure level.
Results: Suboptimal breastfeeding elevated the risk of pneumonia morbidity and mortality outcomes across age groups. In particular, pneumonia mortality was higher among not breastfed compared to exclusively breastfed infants 0-5 months of age (RR: 14.97; 95% CI: 0.67-332.74) and among not breastfed compared to breastfed infants and young children 6-23 months of age (RR: 1.92; 95% CI: 0.79-4.68).
Conclusions: Our results highlight the importance of breastfeeding during the first 23 months of life as a key intervention for reducing pneumonia morbidity and mortality.
Figures
References
-
- Liu L, Johnson HL, Cousens S, Perin J, Scott S, Lawn JE, Rudan I, Campbell H, Cibulskis R, Li M. et al. Global, regional, and national causes of child mortality: an updated systematic analysis for 2010 with time trends since 2000. Lancet. 2012;379(9832):2151–2161. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60560-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nair H, Simoes E, Rudan I, Gessner B, Azziz-Baumgartner E, Zhang JS, Feikin D, Mackenzie G, Moisi J, Roca A. et al. Global and regional estimates of hospitalised severe acute lower respiratory infections in young children in 2010: a systematic review and meta analysis. Lancet. 2013;381(9875):1380–1390. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61901-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases