Molecular mechanisms of neutrophil dysfunction in glycogen storage disease type Ib
- PMID: 24565827
- PMCID: PMC4007611
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2013-05-502435
Molecular mechanisms of neutrophil dysfunction in glycogen storage disease type Ib
Abstract
Glycogen storage disease type Ib (GSD-Ib) is an autosomal-recessive syndrome characterized by neutropenia and impaired glucose homeostasis resulting from a deficiency in the glucose-6-phosphate (G6P) transporter (G6PT). The underlying cause of GSD-Ib neutropenia is an enhanced neutrophil apoptosis, but patients also manifest neutrophil dysfunction of unknown etiology. Previously, we showed G6PT interacts with the enzyme glucose-6-phosphatase-β (G6Pase-β) to regulate the availability of G6P/glucose in neutrophils. A deficiency in G6Pase-β activity in neutrophils impairs both their energy homeostasis and function. We now show that G6PT-deficient neutrophils from GSD-Ib patients are similarly impaired. Their energy impairment is characterized by decreased glucose uptake and reduced levels of intracellular G6P, lactate, adenosine triphosphate, and reduced NAD phosphate, whereas functional impairment is reflected in reduced neutrophil respiratory burst, chemotaxis, and calcium mobilization. We further show that the mechanism of neutrophil dysfunction in GSD-Ib arises from activation of the hypoxia-inducible factor-1α/peroxisome-proliferators-activated receptor-γ pathway.
Figures

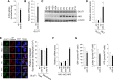
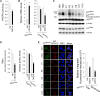

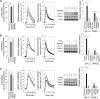

Comment in
-
Neutrophil energetics and oxygen sensing.Blood. 2014 May 1;123(18):2753-4. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-03-560409. Blood. 2014. PMID: 24786455
References
-
- Pan C-J, Lin B, Chou JY. Transmembrane topology of human glucose 6-phosphate transporter. J Biol Chem. 1999;274(20):13865–13869. - PubMed
-
- Lei K-J, Shelly LL, Pan C-J, Sidbury JB, Chou JY. Mutations in the glucose-6-phosphatase gene that cause glycogen storage disease type 1a. Science. 1993;262(5133):580–583. - PubMed
-
- Shieh J-J, Pan C-J, Mansfield BC, Chou JY. A glucose-6-phosphate hydrolase, widely expressed outside the liver, can explain age-dependent resolution of hypoglycemia in glycogen storage disease type Ia. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(47):47098–47103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

