Evaluation of the potential of antipsychotic agents to induce catalepsy in rats: assessment of a new, commercially available, semi-automated instrument
- PMID: 24565832
- PMCID: PMC3992273
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pbb.2014.02.013
Evaluation of the potential of antipsychotic agents to induce catalepsy in rats: assessment of a new, commercially available, semi-automated instrument
Abstract
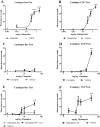
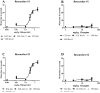
Haloperidol induced catalepsy was determined using the classic bar test and a new MED Associates Catalepsy Test Chamber instrument. The dose that produced an adverse effect in 50% of rats (AED50) for haloperidol was calculated using the instrument data as 0.29 mg/kg. Hand scoring of the video recordings gave AED50 values of 0.30 and 0.31 mg/kg, both well within the 95% CL of the instrument data. Clozapine was also evaluated and catalepsy was not detected up to 40 mg/kg. No significant difference was found between the instrument and hand scoring data. The instrument was useful for testing haloperidol and clozapine, relieving much of the tedium and variability experienced without its use. It was especially valuable at measuring shorter time periods, where the researcher cannot react as quickly. Finally, olanzapine was also evaluated. However, clenched forepaws and hind paws prevented the use of the instrument alone at higher doses. A backup stopwatch was used for the bar test in these cases. Some of the advantages and limitations are discussed. Results are also compared to the crossed-legs position (CLP) test for all three antipsychotics. While haloperidol gave similar results at all concentrations tested, clozapine deviated significantly at the highest dose (40 mg/kg) displaying catalepsy in the CLP test but not in the bar test. Olanzapine displayed catalepsy in rats significantly different from vehicle at 40 mg/kg in both the bar and CLP tests. However, the CLP test may be more suited to compounds with gripping problems which prevent the consistent grasping of the bar. Overall, the instrument was found to be a useful aid in conducting the bar test for catalepsy. The CLP test was found to complement the bar test under certain conditions and could provide additional data that might be missed by the bar test for compounds producing grasping problems.
Keywords: Atypical antipsychotics; Bar test for catalepsy; Catalepsy instrument; Crossed-leg position (CLP) test; Extrapyramidal side effect (EPS); Typical antipsychotics.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures

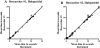
References
-
- Ablordeppey SY, Altundas R, Bricker B, Zhu XY, Suresh Kumar EVK, Jackson T, Khan A, Roth BL. Identification of A Butyrophenone Analog as a Potential Atypical Antipsychotic Agent: 4-[4-(4-Chlorophenyl)-1,4-diazepan-1-yl]-1-(4-fluorophenyl)butan-1-one. Bioorg Med Chem. 2008;16:7291–7301. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alvarez-Cervera FJ, Villanueva-Toledo J, Moo-Puc RE, Heredia-Lopez FJ, Alvarez-Cervera M, Pineda JC, Gongora-Alfaro JL. A novel automated rat catalepsy bar test system based on a RISC microcontroller. J Neuroscience Methods. 2005;146:76–83. - PubMed
-
- Bardin L, Auclair A, Kleven MS, Prinssen EPM, Koek W, Newman-Tancredi A, Depoortere R. Pharmacological profiles in rats of novel antipsychotics with combined dopamine D2/serotonin 5-HT1A activity: comparison with typical and atypical conventional antipsychotics. Behav Pharmacol. 2007;18:103–18. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

