Managing patients with psoriatic disease: the diagnosis and pharmacologic treatment of psoriatic arthritis in patients with psoriasis
- PMID: 24566842
- PMCID: PMC3958815
- DOI: 10.1007/s40265-014-0191-y
Managing patients with psoriatic disease: the diagnosis and pharmacologic treatment of psoriatic arthritis in patients with psoriasis
Abstract
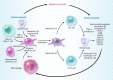
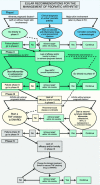
Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a chronic, systemic inflammatory disease. Up to 40 % of patients with psoriasis will go on to develop PsA, usually within 5-10 years of cutaneous disease onset. Both conditions share common pathogenic mechanisms involving genetic and environmental factors. Because psoriasis is typically present for years before PsA-related joint symptoms emerge, dermatologists are in a unique position to detect PsA earlier in the disease process through regular, routine screening of psoriasis patients. Distinguishing clinical features of PsA include co-occurrence of psoriatic skin lesions and nail dystrophy, as well as dactylitis and enthesitis. Patients with PsA are usually seronegative for rheumatoid factor, and radiographs may reveal unique features such as juxta-articular new bone formation and pencil-in-cup deformity. Early treatment of PsA with disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs has the potential to slow disease progression and maintain patient quality of life. Optimally, a single therapeutic agent will control both the skin and joint psoriatic symptoms. A number of traditional treatments used to manage psoriasis, such as methotrexate and cyclosporine, are also effective for PsA, but these agents are often inadequately effective, temporary in benefit and associated with significant safety concerns. Biologic anti-tumour necrosis factor agents, such as etanercept, infliximab and adalimumab, are effective for treating patients who have both psoriasis and PsA. However, a substantial number of patients may lose efficacy, have adverse effects or find intravenous or subcutaneous administration inconvenient. Emerging oral treatments, including phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors, such as apremilast, and new biologics targeting interleukin-17, such as secukinumab, brodalumab and ixekizumab, have shown encouraging clinical results in the treatment of psoriasis and/or PsA. Active and regular collaboration of dermatologists with rheumatologists in managing patients who have psoriasis and PsA is likely to yield more optimal control of psoriatic dermal and joint symptoms, and improve long-term patient outcomes.
Figures

References
-
- Nestle FO, Kaplan DH, Barker J. Psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(5):496–509. - PubMed
-
- Menter A, Gottlieb A, Feldman SR, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: section 1. Overview of psoriasis and guidelines of care for the treatment of psoriasis with biologics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58(5):826–850. - PubMed
-
- Chang CA, Gottlieb AB, Lizzul PF. Management of psoriatic arthritis from the view of the dermatologist. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7(10):588–598. - PubMed
-
- Augustin M, Reich K, Glaeske G, et al. Co-morbidity and age-related prevalence of psoriasis: analysis of health insurance data in Germany. Acta Derm Venereol. 2010;90(2):147–151. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

