The Solanum lycopersicum Zinc Finger2 cysteine-2/histidine-2 repressor-like transcription factor regulates development and tolerance to salinity in tomato and Arabidopsis
- PMID: 24567191
- PMCID: PMC3982756
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.113.225920
The Solanum lycopersicum Zinc Finger2 cysteine-2/histidine-2 repressor-like transcription factor regulates development and tolerance to salinity in tomato and Arabidopsis
Abstract
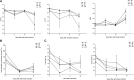
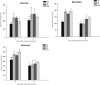
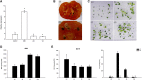
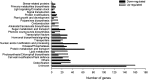
The zinc finger superfamily includes transcription factors that regulate multiple aspects of plant development and were recently shown to regulate abiotic stress tolerance. Cultivated tomato (Solanum lycopersicum Zinc Finger2 [SIZF2]) is a cysteine-2/histidine-2-type zinc finger transcription factor bearing an ERF-associated amphiphilic repression domain and binding to the ACGTCAGTG sequence containing two AGT core motifs. SlZF2 is ubiquitously expressed during plant development, and is rapidly induced by sodium chloride, drought, and potassium chloride treatments. Its ectopic expression in Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) and tomato impaired development and influenced leaf and flower shape, while causing a general stress visible by anthocyanin and malonyldialdehyde accumulation. SlZF2 enhanced salt sensitivity in Arabidopsis, whereas SlZF2 delayed senescence and improved tomato salt tolerance, particularly by maintaining photosynthesis and increasing polyamine biosynthesis, in salt-treated hydroponic cultures (125 mm sodium chloride, 20 d). SlZF2 may be involved in abscisic acid (ABA) biosynthesis/signaling, because SlZF2 is rapidly induced by ABA treatment and 35S::SlZF2 tomatoes accumulate more ABA than wild-type plants. Transcriptome analysis of 35S::SlZF2 revealed that SlZF2 both increased and reduced expression of a comparable number of genes involved in various physiological processes such as photosynthesis, polyamine biosynthesis, and hormone (notably ABA) biosynthesis/signaling. Involvement of these different metabolic pathways in salt stress tolerance is discussed.
Figures




Similar articles
-
SlDREB2, a tomato dehydration-responsive element-binding 2 transcription factor, mediates salt stress tolerance in tomato and Arabidopsis.Plant Cell Environ. 2016 Jan;39(1):62-79. doi: 10.1111/pce.12591. Epub 2015 Aug 8. Plant Cell Environ. 2016. PMID: 26082265
-
A tomato bZIP transcription factor, SlAREB, is involved in water deficit and salt stress response.Planta. 2010 May;231(6):1459-73. doi: 10.1007/s00425-010-1147-4. Epub 2010 Apr 1. Planta. 2010. PMID: 20358223
-
The abiotic stress-responsive NAC-type transcription factor SlNAC4 regulates salt and drought tolerance and stress-related genes in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum).Plant Cell Rep. 2014 Nov;33(11):1851-63. doi: 10.1007/s00299-014-1662-z. Epub 2014 Jul 26. Plant Cell Rep. 2014. PMID: 25063324
-
Phenotyping in Arabidopsis and Crops-Are We Addressing the Same Traits? A Case Study in Tomato.Genes (Basel). 2020 Aug 27;11(9):1011. doi: 10.3390/genes11091011. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32867311 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Pathways of WRKY Genes in Regulating Plant Salinity Tolerance.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 19;23(18):10947. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810947. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142857 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The C2H2 zinc-finger protein SlZF3 regulates AsA synthesis and salt tolerance by interacting with CSN5B.Plant Biotechnol J. 2018 Jun;16(6):1201-1213. doi: 10.1111/pbi.12863. Epub 2017 Dec 28. Plant Biotechnol J. 2018. PMID: 29193661 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Analyses of the Genetic Screening of C2H2-Type Zinc Finger Transcription Factors and Abiotic and Biotic Stress Responses in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) Based on RNA-Seq Data.Front Genet. 2020 May 28;11:540. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00540. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 32547602 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of multiprotein bridging factor 1 family genes and SlMBF1c negatively regulate the resistance to Botrytis cinerea in tomato.BMC Plant Biol. 2019 Oct 21;19(1):437. doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-2029-y. BMC Plant Biol. 2019. PMID: 31638895 Free PMC article.
-
SpPKE1, a Multiple Stress-Responsive Gene Confers Salt Tolerance in Tomato and Tobacco.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 May 20;20(10):2478. doi: 10.3390/ijms20102478. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31137458 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular genetic analyses of abiotic stress responses during plant reproductive development.J Exp Bot. 2020 May 30;71(10):2870-2885. doi: 10.1093/jxb/eraa089. J Exp Bot. 2020. PMID: 32072177 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agarwal P, Arora R, Ray S, Singh AK, Singh VP, Takatsuji H, Kapoor S, Tyagi AK. (2007) Genome-wide identification of C2H2 zinc-finger gene family in rice and their phylogeny and expression analysis. Plant Mol Biol 65: 467–485 - PubMed
-
- Borghesi E, González-Miret ML, Escudero-Gilete ML, Malorgio F, Heredia FJ, Meléndez-Martínez AJ. (2011) Effects of salinity stress on carotenoids, anthocyanins, and color of diverse tomato genotypes. J Agric Food Chem 59: 11676–11682 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

