Mortality associated with seasonal and pandemic influenza and respiratory syncytial virus among children <5 years of age in a high HIV prevalence setting--South Africa, 1998-2009
- PMID: 24567249
- PMCID: PMC9096151
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciu095
Mortality associated with seasonal and pandemic influenza and respiratory syncytial virus among children <5 years of age in a high HIV prevalence setting--South Africa, 1998-2009
Abstract
Background: There are few published data describing the mortality burden associated with influenza and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection in children in low- and middle-income countries and particularly from Africa and settings with high prevalence of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
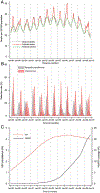
Methods: We modeled the excess mortality attributable to influenza (seasonal and pandemic) and RSV infection by applying Poisson regression models to monthly all-respiratory and pneumonia and influenza deaths, using national influenza and RSV laboratory surveillance data as covariates. In addition, we estimated the seasonal influenza- and RSV-associated deaths among HIV-infected and -uninfected children using Poisson regression models that incorporated HIV prevalence and highly active antiretroviral therapy coverage as covariates.
Results: In children <5 years of age, the mean annual numbers of seasonal influenza- and RSV-associated all-respiratory deaths were 452 (8 per 100 000 person-years [PY]) and 546 (10 per 100 000 PY), respectively. Infants <1 year of age experienced higher mortality rates compared with children 1-4 years of age for both influenza (22 vs 5 per 100 000 PY) and RSV (35 vs 4 per 100 000 PY). HIV-infected compared with HIV-uninfected children <5 years of age were at increased risk of death associated with influenza (age-adjusted relative risk [aRR], 11.5; 95% confidence interval [CI], 9.6-12.6) and RSV (aRR, 8.1; 95% CI, 6.9-9.3) infection. In 2009, we estimated 549 (11 per 100 000 PY) all-respiratory influenza A(H1N1)pdm09-associated deaths among children aged <5 years.
Conclusions: Our findings support increased research efforts to guide and prioritize interventions such as influenza vaccination and HIV prevention in low- and middle-income countries with high HIV prevalence such as South Africa.
Keywords: HIV; South Africa; influenza; mortality; respiratory syncytial virus.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. Conflicts that the editors consider relevant to the content of the manuscript have been disclosed.
Figures
References
-
- Liu L, Johnson HL, Cousens S, et al. Global, regional, and national causes of child mortality: an updated systematic analysis for 2010 with time trends since 2000. Lancet 2012; 379:2151–61. - PubMed
-
- Simonsen L, Clarke MJ, Schonberger LB, et al. Pandemic versus epidemic influenza mortality: a pattern of changing age distribution. J Infect Dis 1998; 178:53–60. - PubMed
-
- Thompson WW, Shay DK, Weintraub E, et al. Mortality associated with influenza and respiratory syncytial virus in the United States. JAMA 2003; 289:179–86. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

