Coordinated nuclear and synaptic shuttling of afadin promotes spine plasticity and histone modifications
- PMID: 24567331
- PMCID: PMC4036196
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.536391
Coordinated nuclear and synaptic shuttling of afadin promotes spine plasticity and histone modifications
Abstract
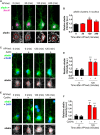
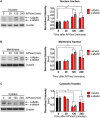
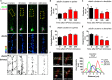
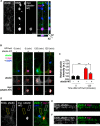
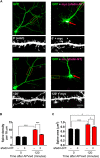
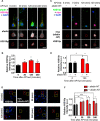
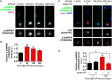
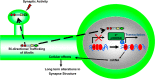
The ability of a neuron to transduce extracellular signals into long lasting changes in neuronal morphology is central to its normal function. Increasing evidence shows that coordinated regulation of synaptic and nuclear signaling in response to NMDA receptor activation is crucial for long term memory, synaptic tagging, and epigenetic signaling. Although mechanisms have been proposed for synapse-to-nuclear communication, it is unclear how signaling is coordinated at both subcompartments. Here, we show that activation of NMDA receptors induces the bi-directional and concomitant shuttling of the scaffold protein afadin from the cytosol to the nucleus and synapses. Activity-dependent afadin nuclear translocation peaked 2 h post-stimulation, was independent of protein synthesis, and occurred concurrently with dendritic spine remodeling. Moreover, activity-dependent afadin nuclear translocation coincides with phosphorylation of histone H3 at serine 10 (H3S10p), a marker of epigenetic modification. Critically, blocking afadin nuclear accumulation attenuated activity-dependent dendritic spine remodeling and H3 phosphorylation. Collectively, these data support a novel model of neuronal nuclear signaling whereby dual-residency proteins undergo activity-dependent bi-directional shuttling from the cytosol to synapses and the nucleus, coordinately regulating dendritic spine remodeling and histone modifications.
Keywords: AF-6; Cell Biology; Chromatin Histone Modification; Dendritic Spine; Neurobiology; Nucleus; Signaling; Small GTPase; Synapses; Synaptic Plasticity.
Figures

References
-
- Jordan B. A., Kreutz M. R. (2009) Nucleocytoplasmic protein shuttling: The direct route in synapse-to-nucleus signaling. Trends Neurosci. 32, 392–401 - PubMed
-
- Greer P. L., Greenberg M. E. (2008) From synapse to nucleus: Calcium-dependent gene transcription in the control of synapse development and function. Neuron 59, 846–860 - PubMed
-
- Berger S. L. (2007) The complex language of chromatin regulation during transcription. Nature 447, 407–412 - PubMed
-
- Riccio A. (2010) Dynamic epigenetic regulation in neurons: Enzymes, stimuli and signaling pathways. Nat. Neurosci. 13, 1330–1337 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 1F31NS076201/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH097216/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- DA013141-11A1/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA013141/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- 1F31MH087043/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- F31 MH087043/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MR/L021064/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- F31 MH085362/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH097216/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 1F31MH085362/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- F31 NS076201/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- MH071316/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH071316/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

