Examining how enzymes self-organize in a membrane
- PMID: 24567406
- PMCID: PMC3956151
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1401325111
Examining how enzymes self-organize in a membrane
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
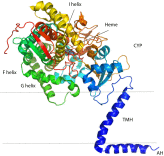
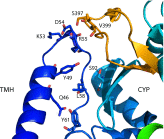

Comment on
-
Architecture of a single membrane spanning cytochrome P450 suggests constraints that orient the catalytic domain relative to a bilayer.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Mar 11;111(10):3865-70. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1324245111. Epub 2014 Feb 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24613931 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

