X-ray structural and biological evaluation of a series of potent and highly selective inhibitors of human coronavirus papain-like proteases
- PMID: 24568342
- PMCID: PMC3983375
- DOI: 10.1021/jm401712t
X-ray structural and biological evaluation of a series of potent and highly selective inhibitors of human coronavirus papain-like proteases
Abstract
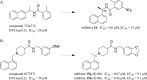
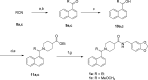
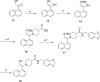
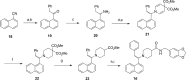
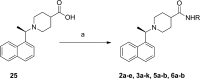
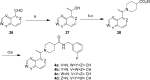
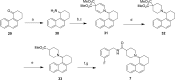
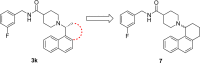
Structure-guided design was used to generate a series of noncovalent inhibitors with nanomolar potency against the papain-like protease (PLpro) from the SARS coronavirus (CoV). A number of inhibitors exhibit antiviral activity against SARS-CoV infected Vero E6 cells and broadened specificity toward the homologous PLP2 enzyme from the human coronavirus NL63. Selectivity and cytotoxicity studies established a more than 100-fold preference for the coronaviral enzyme over homologous human deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs), and no significant cytotoxicity in Vero E6 and HEK293 cell lines is observed. X-ray structural analyses of inhibitor-bound crystal structures revealed subtle differences between binding modes of the initial benzodioxolane lead (15g) and the most potent analogues 3k and 3j, featuring a monofluoro substitution at para and meta positions of the benzyl ring, respectively. Finally, the less lipophilic bis(amide) 3e and methoxypyridine 5c exhibit significantly improved metabolic stability and are viable candidates for advancing to in vivo studies.
Figures

References
-
- Summary Table of SARS Cases by Country, 1 November 2002–7 August 2003. WHO: Geneva, August 15, 2003; http://www.who.int/csr/sars/country/2003_08_15/en/.
-
- van Boheemen S.; Zaki A. M.; Bestebroer T. M.; de Graaf M.; Victor S.; Osterhaus A. D.; Haagmans B. L.; Fouchier R. A.. Genomic Analysis for a Newly Isolated Human Betacoronavirus Lineage 2C. Submitted Sep 26, 2012.
- Bermingham A.; Chand M.; Brown C.; Aarons E.; Tong C.; Langrish C.; Hoschler K.; Brown K.; Galiano M.; Myers R.; Pebody R.; Green H.; Boddington N.; Gopal R.; Price N.; Newsholme W.; Drosten C.; Fouchier R.; Zambon M. Severe respiratory illness caused by a novel coronavirus, in a patient transferred to the United Kingdom from the Middle East, September 2012. Eurosurveillance 2012, 1740pii=20290. - PubMed
- Pebody R. G.; Chand M. A.; Thomas H. L.; Green H. K.; Boddington N. L.; Carvalho C.; Brown C. S.; Anderson S. R.; Rooney C.; Crawley-Boevey E.; Irwin D. J.; Aarons E.; Tong C.; Newsholme W.; Price N.; Langrish C.; Tucker D.; Zhao H.; Phin N.; Crofts J.; Bermingham A.; Gilgunn-Jones E.; Brown K. E.; Evans B.; Catchpole M.; Watson J. M. The United Kingdom public health response to an imported laboratory confirmed case of a novel coronavirus in September 2012. Eurosurveillance 2012, 174020292. - PubMed
-
- de Groot R. J.; Baker S. C.; Baric R. S.; Brown C. S.; Drosten C.; Enjuanes L.; Fouchier R. A.; Galiano M.; Gorbalenya A. E.; Memish Z.; Perlman S.; Poon L. L.; Snijder E. J.; Stephens G. M.; Woo P. C.; Zaki A. M.; Zambon M.; Ziebuhr J. Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV): Announcement of the Coronavirus Study Group. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 7790–7792. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kindler E.; Jonsdottir H. R.; Muth D.; Hamming O. J.; Hartmann R.; Rodriguez R.; Geffers R.; Fouchier R. A.; Drosten C.; Muller M. A.; Dijkman R.; Thiel V. Efficient Replication of the Novel Human Betacoronavirus EMC on Primary Human Epithelium Highlights Its Zoonotic Potential. mBio 2013, 41e00611-12. - PMC - PubMed
-
- van Boheemen S.; de Graaf M.; Lauber C.; Bestebroer T. M.; Raj V. S.; Zaki A. M.; Osterhaus A. D.; Haagmans B. L.; Gorbalenya A. E.; Snijder E. J.; Fouchier R. A. Genomic characterization of a newly discovered coronavirus associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome in humans. mBio 2012, 36e00473-12. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

