Intraocular pressure-lowering efficacy and safety of bimatoprost 0.03% therapy for primary open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension patients in China
- PMID: 24568617
- PMCID: PMC3943806
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2415-14-21
Intraocular pressure-lowering efficacy and safety of bimatoprost 0.03% therapy for primary open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension patients in China
Abstract
Background: To report the clinical outcomes in Chinese patients with primary open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension treated with bimatoprost 0.03% therapy.
Methods: Two hundred sixty-three Chinese patients with primary open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension who needed initial or additional intraocular pressure (IOP) lowering were recruited in this prospective, open-label, multicenter clinical study and were treated with bimatoprost 0.03%. Patients received bimatoprost 0.03% as initial, replacement or adjunctive IOP-lowering therapy, and follow-up visits were performed at week 1, and month 1 and 3 of the bimatoprost treatment. The efficacy outcome measure was the post-treatment IOP level. The safety outcome measures included the rate of medication-related symptoms, physical signs, reported adverse events, and the level of conjunctival hyperemia.
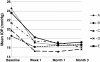
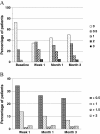
Results: Among 240 patients who could be categorized by pre-existing therapies and the bimatoprost therapy regimen in the study, IOP values observed in all medication conditions showed significant IOP reduction at all study visits compared with baseline. At 3 months, 8.0 ± 3.7 mmHg (32.0%) reduction in IOP was observed in treatment-naive patients after bimatoprost monotherapy; in the patients previously on various therapy regimens, 1.9 ± 2.8 mmHg (9.5%) to 6.4 ± 6.1 mmHg (24.8%) additional IOP lowering was achieved after switching to bimatoprost monotherapy or bimatoprost combination therapy. The most common adverse event was conjunctival hyperemia, mainly of trace and mild intensity.
Conclusions: Our results show that bimatoprost 0.03% was effective in lowering IOP with favorable safety in Chinese primary open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bimatoprost 0.01% in treatment-naïve patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension: an observational study in the Korean clinical setting.BMC Ophthalmol. 2014 Dec 17;14:160. doi: 10.1186/1471-2415-14-160. BMC Ophthalmol. 2014. PMID: 25519810 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and efficacy of bimatoprost/timolol fixed combination in Chinese patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension.Chin Med J (Engl). 2014;127(5):905-10. Chin Med J (Engl). 2014. PMID: 24571886 Clinical Trial.
-
Late-day intraocular pressure-lowering efficacy and tolerability of travoprost 0.004% versus bimatoprost 0.01% in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension: a randomized trial.BMC Ophthalmol. 2014 Nov 28;14:151. doi: 10.1186/1471-2415-14-151. BMC Ophthalmol. 2014. PMID: 25432143 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Topical bimatoprost: a review of its use in open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension.Drugs Aging. 2002;19(3):231-48. doi: 10.2165/00002512-200219030-00008. Drugs Aging. 2002. PMID: 12027782 Review.
-
Bimatoprost - a review.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2009 Nov;10(16):2759-68. doi: 10.1517/14656560903292649. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2009. PMID: 19874254 Review.
Cited by
-
Orbital Fat Volume After Treatment with Topical Prostaglandin Agonists.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020 May 11;61(5):46. doi: 10.1167/iovs.61.5.46. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020. PMID: 32455434 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment with bimatoprost for exophthalmos in patients with inactive thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy.Clin Ophthalmol. 2018 Nov 27;12:2415-2421. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S187164. eCollection 2018. Clin Ophthalmol. 2018. PMID: 30568419 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of glaucoma management with monotherapy medications in Egypt.J Adv Pharm Technol Res. 2017 Jan-Mar;8(1):25-28. doi: 10.4103/2231-4040.197384. J Adv Pharm Technol Res. 2017. PMID: 28217551 Free PMC article.
-
Fixed-combination treatments for intraocular hypertension in Chinese patients - focus on bimatoprost-timolol.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 May 13;9:2617-25. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S80338. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 25999695 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adduction-Induced Strain on the Optic Nerve in Primary Open Angle Glaucoma at Normal Intraocular Pressure.Curr Eye Res. 2021 Apr;46(4):568-578. doi: 10.1080/02713683.2020.1817491. Epub 2020 Sep 11. Curr Eye Res. 2021. PMID: 32911989 Free PMC article.
References
-
- AGIS Investigators. The Advanced Glaucoma Intervention Study (AGIS): 7. The relationship between control of intraocular pressure and visual field deterioration. Am J Ophthalmol. 2000;130:429–440. - PubMed
-
- Kass MA, Heuer DK, Higginbotham EJ, Johnson CA, Keltner JL, Miller JP, Parrish RK 2nd, Wilson MR, Gordon MO. The Ocular Hypertension Treatment Study: a randomized trial determines that topical ocular hypotensive medication delays or prevents the onset of primary open-angle glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 2002;120:701–713. doi: 10.1001/archopht.120.6.701. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

