Mitochondrial damage-associated molecular patterns and vascular function
- PMID: 24569027
- PMCID: PMC4012709
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehu047
Mitochondrial damage-associated molecular patterns and vascular function
Abstract
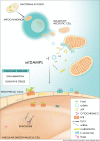
Immune system activation occurs not only due to foreign stimuli, but also due to endogenous molecules. As such, endogenous molecules that are released into the circulation due to cell death and/or injury alarm the immune system that something has disturbed homeostasis and a response is needed. Collectively, these molecules are known as damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs). Mitochondrial DAMPs (mtDAMPs) are potent immunological activators due to the bacterial ancestry of mitochondria. Mitochondrial DAMPs are recognized by specific pattern recognition receptors of the innate immune system, some of which are expressed in the cardiovascular system. Cell death leads to release of mtDAMPs that may induce vascular changes by mechanisms that are currently not well understood. This review will focus on recently published evidence linking mtDAMPs and immune system activation to vascular dysfunction and cardiovascular disease.
Keywords: Cardiovascular disease; Damage-associated molecular patterns; Immune system; Mitochondria; Vascular function.
Figures
References
-
- Sagan L. On the origin of mitosing cells. J Theor Biol. 1967;14:255–274. - PubMed
-
- Margulis L, Bermudes D. Symbiosis as a mechanism of evolution: status of cell symbiosis theory. Symbiosis. 1985;1:101–124. - PubMed
-
- Matzinger P. Tolerance, danger, and the extended family. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:991–1045. - PubMed
-
- Krysko DV, Agostinis P, Krysko O, Garg AD, Bachert C, Lambrecht BN, Vandenabeele P. Emerging role of damage-associated molecular patterns derived from mitochondria in inflammation. Trends Immunol. 2011;32:157–164. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

