Neuroendocrine signaling via the serotonin transporter regulates clearance of apoptotic cells
- PMID: 24570000
- PMCID: PMC4036168
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.482299
Neuroendocrine signaling via the serotonin transporter regulates clearance of apoptotic cells
Abstract
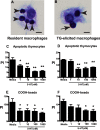
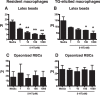
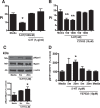
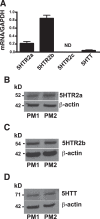
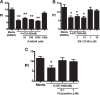
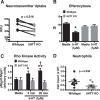
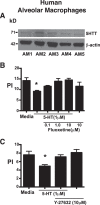
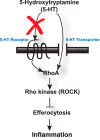
Serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine; 5-HT) is a CNS neurotransmitter increasingly recognized to exert immunomodulatory effects outside the CNS that contribute to the pathogenesis of autoimmune and chronic inflammatory diseases. 5-HT signals to activate the RhoA/Rho kinase (ROCK) pathway, a pathway known for its ability to regulate phagocytosis. The clearance of apoptotic cells (i.e. efferocytosis) is a key modulator of the immune response that is inhibited by the RhoA/ROCK pathway. Because efferocytosis is defective in many of the same illnesses where 5-HT has been implicated in disease pathogenesis, we hypothesized that 5-HT would suppress efferocytosis via activation of RhoA/ROCK. The effect of 5-HT on efferocytosis was examined in murine peritoneal and human alveolar macrophages, and its mechanisms were investigated using pharmacologic blockade and genetic deletion. 5-HT impaired efferocytosis by murine peritoneal macrophages and human alveolar macrophages. 5-HT increased phosphorylation of myosin phosphatase subunit 1 (Mypt-1), a known ROCK target, and inhibitors of RhoA and ROCK reversed the suppressive effect of 5-HT on efferocytosis. Peritoneal macrophages expressed the 5-HT transporter and 5-HT receptors (R) 2a, 2b, but not 2c. Inhibition of 5-HTR2a and 5-HTR2b had no effect on efferocytosis, but blockade of the 5-HT transporter prevented 5-HT-impaired efferocytosis. Genetic deletion of the 5-HT transporter inhibited 5-HT uptake into peritoneal macrophages, prevented 5-HT-induced phosphorylation of Mypt-1, reversed the inhibitory effect of 5-HT on efferocytosis, and decreased cellular peritoneal inflammation. These results suggest a novel mechanism by which 5-HT might disrupt efferocytosis and contribute to the pathogenesis of autoimmune and chronic inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: Autoimmune Diseases; Efferocytosis; Inflammation; Lung; Phagocytosis; Rho Kinase; RhoA; Serotonin Receptors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Acute and chronic alcohol exposure impair the phagocytosis of apoptotic cells and enhance the pulmonary inflammatory response.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2010 Oct;34(10):1723-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2010.01259.x. Epub 2010 Jul 1. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2010. PMID: 20608904 Free PMC article.
-
Cigarette smoke impairs clearance of apoptotic cells through oxidant-dependent activation of RhoA.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009 Jun 1;179(11):1011-21. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200807-1148OC. Epub 2009 Mar 5. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009. PMID: 19264974 Free PMC article.
-
Crystalline Silica Impairs Efferocytosis Abilities of Human and Mouse Macrophages: Implication for Silica-Associated Systemic Sclerosis.Front Immunol. 2020 Feb 18;11:219. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00219. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32133004 Free PMC article.
-
Statin-regulated phagocytosis and efferocytosis in physiological and pathological conditions.Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Oct;238:108282. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2022.108282. Epub 2022 Sep 18. Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 36130624 Review.
-
Macrophage efferocytosis in health and disease.Cell Biochem Funct. 2023 Mar;41(2):152-165. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3780. Epub 2023 Feb 16. Cell Biochem Funct. 2023. PMID: 36794573 Review.
Cited by
-
The Brain-Skin Connection and the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis: A Review with a Focus on the Serotonergic System.Cells. 2020 Mar 26;9(4):796. doi: 10.3390/cells9040796. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32224981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fluoxetine protects against methamphetamine‑induced lung inflammation by suppressing oxidative stress through the SERT/p38 MAPK/Nrf2 pathway in rats.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Feb;15(2):673-680. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.6072. Epub 2016 Dec 23. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28035393 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Depression-The Vicious Mental Cycle.Healthcare (Basel). 2025 Jul 15;13(14):1699. doi: 10.3390/healthcare13141699. Healthcare (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40724725 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interactions Between the Serotonergic and Other Neurotransmitter Systems in the Basal Ganglia: Role in Parkinson's Disease and Adverse Effects of L-DOPA.Front Neuroanat. 2020 Jun 4;14:26. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2020.00026. eCollection 2020. Front Neuroanat. 2020. PMID: 32581728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomic and bioinformatics profile of paired human alveolar macrophages and peripheral blood monocytes.Proteomics. 2015 Nov;15(22):3797-805. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201400496. Proteomics. 2015. PMID: 26389541 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mössner R., Lesch K. P. (1998) Role of serotonin in the immune system and in neuroimmune interactions. Brain Behav. Immun. 12, 249–271 - PubMed
-
- Walther D. J., Stahlberg S., Vowinckel J. (2011) Novel roles for biogenic monoamines: from monoamines in transglutaminase-mediated post-translational protein modification to monoaminylation deregulation diseases. FEBS J. 278, 4740–4755 - PubMed
-
- Walther D. J., Peter J. U., Winter S., Höltje M., Paulmann N., Grohmann M., Vowinckel J., Alamo-Bethencourt V., Wilhelm C. S., Ahnert-Hilger G., Bader M. (2003) Serotonylation of small GTPases is a signal transduction pathway that triggers platelet α-granule release. Cell 115, 851–862 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

