Synthesis, Anti-Inflammatory and Anti- Nociceptive Activities and Cytotoxic Effect of Novel Thiazolidin-4-ones Derivatives as Selective Cyclooxygenase (COX-2) Inhibitors
- PMID: 24570829
- PMCID: PMC3933800
Synthesis, Anti-Inflammatory and Anti- Nociceptive Activities and Cytotoxic Effect of Novel Thiazolidin-4-ones Derivatives as Selective Cyclooxygenase (COX-2) Inhibitors
Abstract
Objective(s): Nowadays, COX - 2 inhibitors such as valdecoxib are removed from the market because of their cardiovascular toxicity and their potential to increase the risk of strokes. In response to this, medicinal chemists have attempted to synthesize new classes of COX-2 Inhibitors.
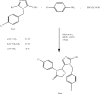
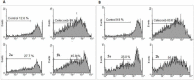
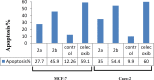
Materials and methods: In this study, three novel analogues of thiazolidin-4-ones derivatives 2a-c were synthesized. The ability of these compounds to inhibit ovine COX-1 and COX-2 (0.2- 0.8 µM) was determined using a colorimetric method. The cytotoxic effect of the synthesized compounds (25-100 M) was also investigated by measuring their cytotoxicity against Caco-2 and MCF-7 cell lines using MTT assay. Cell apoptosis was determined by flow cytometry. Writhing test (7.5-75 mg/kg) was used to examine the antinociceptive effects in mice. The effect of the analogues against acute inflammation (7.5-75 mg/kg) was also studied using xylene-induced ear edema test in mice.
Results: The synthesized compounds showed a weak capacity to inhibit the proliferation of Caco-2 and MCF-7 cell lines. The COX-2 inhibition potency and selectivity index for test compounds 2a-b were as follows; celecoxib > 2b > 2a. On the other hand, all three analogues exhibited strong antinociceptive activity against acetic acid-induced writhing. The anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive effects of the analogues were markedly more than positive control, celecoxib.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates that the antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activity profiles exhibited by the novel synthesized compounds are independent from their COX-2 inhibitory potencies. The found antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects can be caused by interaction with other target; independent from COX-2. Accordingly, the compounds 2a-c could serve as lead compounds to develop novel anti-inflammation and antinociceptive drugs.
Keywords: Anti-Inflammatory; Anticancer; Antinociceptive; COX-2 inhibitor; Celecoxib; Thiazolidin-4-ones.
Figures
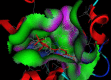
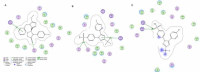
Similar articles
-
New Ferrocene Compounds as Selective Cyclooxygenase (COX-2) Inhibitors: Design, Synthesis, Cytotoxicity and Enzyme-inhibitory Activity.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2018;18(2):295-301. doi: 10.2174/1871520617666171003145533. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 28971779
-
Effect of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors on prostate cancer cell proliferation.Anticancer Res. 2003 Sep-Oct;23(5A):3923-8. Anticancer Res. 2003. PMID: 14666698
-
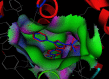
Aryl/heteroaryl Substituted Celecoxib Derivatives as COX-2 Inhibitors: Synthesis, Anti-inflammatory Activity and Molecular Docking Studies.Med Chem. 2017;13(5):484-497. doi: 10.2174/1573406413666170221093740. Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28228088
-
New 1,2,4-triazole/pyrazole hybrids linked to oxime moiety as nitric oxide donor celecoxib analogs: Synthesis, cyclooxygenase inhibition anti-inflammatory, ulcerogenicity, anti-proliferative activities, apoptosis, molecular modeling and nitric oxide release studies.Bioorg Chem. 2020 May;98:103752. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.103752. Epub 2020 Mar 12. Bioorg Chem. 2020. PMID: 32197148
-
Evaluation of 2 celecoxib derivatives: analgesic effect and selectivity to cyclooxygenase-2/1.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2005 Dec;26(12):1505-11. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7254.2005.00222.x. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2005. PMID: 16297351
Cited by
-
Anti-nociceptive and Anti-inflammatory Activities of Asparacosin A Involve Selective Cyclooxygenase 2 and Inflammatory Cytokines Inhibition: An in-vitro, in-vivo, and in-silico Approach.Front Immunol. 2019 Mar 26;10:581. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00581. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30972073 Free PMC article.
-
Analgesic effect of Persian Gulf Conus textile venom.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2014 Oct;17(10):793-7. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2014. PMID: 25729549 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological effects of a synthetic quinoline, a hybrid of tomoxiprole and naproxen, against acute pain and inflammation in mice: a behavioral and docking study.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2017 Apr;20(4):446-450. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2017.8588. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 28804615 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-inflammatory activity of anti-hyperlipidemic drug, fenofibrate, and its phase-I metabolite fenofibric acid: in silico, in vitro, and in vivo studies.Inflammopharmacology. 2018 Aug;26(4):973-981. doi: 10.1007/s10787-017-0428-y. Epub 2017 Dec 13. Inflammopharmacology. 2018. PMID: 29238904
References
-
- Fletcher BS, Kujubu DA, Perrin DM, Herschman HR. Structure of the mitogen-inducible TIS10 gene and demonstration that the TIS10-encoded protein is a functional prostaglandin G/H synthase. J Biol Chem . 1992;267:4338–4443. - PubMed
-
- Crofford LJ. COX-1 and COX-2 tissue expression: implications and predictions. J Rheumatol . 1997;24:49–52. - PubMed
-
- Coffey RJ, Hawkey CJ, Damstrup L, Graves DR, Daniel VC, Dempsey PJ, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor activation induces nuclear targeting of cyclooxygenase-2, basolateral release of prostaglandins, and mitogenesis in polarizing colon cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA . 1997;94:657–662. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mitchell JA, Evans TW. Cyclooxygenase-2 as a therapeutic target. Inflamm Res . 1998;47:88–92. - PubMed
-
- Bijlsma JW, Van de Putte LB. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents (NSAID's) with lesser side effects by selective inhibition of cyclo-oxygenase-2. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd . 1998;142:1762–1765. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
