The Prognosis According to Patterns of Mediastinal Lymph Node Metastasis in Pathologic Stage IIIA/N2 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- PMID: 24570860
- PMCID: PMC3928257
- DOI: 10.5090/kjtcs.2014.47.1.13
The Prognosis According to Patterns of Mediastinal Lymph Node Metastasis in Pathologic Stage IIIA/N2 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study is to evaluate prognostic factors for survival in pathologic stage IIIA/N2 non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), to identify the prognostic significance of the metastatic patterns of mediastinal lymph nodes (MLNs) relating to survival and to recurrence and metastasis.
Methods: A total of 129 patients who underwent radical resection for pathologic stage IIIA-N2 NSCLC from July 1998 to April 2011 were retrospectively reviewed. The end points of this study were rates of loco-regional recurrence and distant metastasis, and survival.
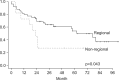
Results: The overall 5-year survival rate was 47.4%. A univariate analysis showed that age, pathologic T stage, and adjuvant chemotherapy were significant prognostic factors, while in multivariate analysis, pathologic T stage and adjuvant chemotherapy were significant prognostic factors. The metastasis rate was higher in patients with multistation N2 involvement and with more than 3 positive MLNs. Further, non-regional MLN metastasis was associated with a higher loco-regional recurrence rate.
Conclusion: Pathologic T stage and adjuvant chemotherapy were independent prognostic factors for long-term survival in pathologic stage IIIA/N2 NSCLC. The recurrence and the metastasis rate were affected by the metastatic patterns of MLNs. These results may be helpful for planning postoperative therapeutic strategies and predicting outcomes.
Keywords: Carcinoma, non-small cell, lung; Lung surgery; Mediastinal lymph nodes; Neoplasm metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

References
-
- Inoue M, Sawabata N, Takeda S, Ohta M, Ohno Y, Maeda H. Results of surgical intervention for p-stage IIIA (N2) non-small cell lung cancer: acceptable prognosis predicted by complete resection in patients with single N2 disease with primary tumor in the upper lobe. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2004;127:1100–1106. - PubMed
-
- Saito M, Kato H. Prognostic factors in patients with pathological and N2 non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2008;14:1–2. - PubMed
-
- Kim DJ, Kim KD, Kim CY, Chung KY. Nodal station as a prognostic factor in resected stage IIIA N2 non-small cell lung cancer. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2003;36:489–496.
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines [Internet] Fort Washington (PA): National Comprehensive Cancer Network; 2013. [cited 2013 Mar 1]. Available from: http://www.nccn.org/index.asp.
-
- Alberts WM American College of Chest Physicians. Diagnosis and management of lung cancer executive summary: ACCP evidence-based clinical practice guidelines (2nd Edition) Chest. 2007;132(3 Suppl):1S–19S. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous