Utilising family-based designs for detecting rare variant disease associations
- PMID: 24571231
- PMCID: PMC4292528
- DOI: 10.1111/ahg.12051
Utilising family-based designs for detecting rare variant disease associations
Abstract
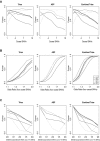
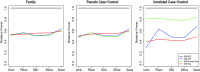
Rare genetic variants are thought to be important components in the causality of many diseases but discovering these associations is challenging. We demonstrate how best to use family-based designs to improve the power to detect rare variant disease associations. We show that using genetic data from enriched families (those pedigrees with greater than one affected member) increases the power and sensitivity of existing case-control rare variant tests. However, we show that transmission- (or within-family-) based tests do not benefit from this enrichment. This means that, in studies where a limited amount of genotyping is available, choosing a single case from each of many pedigrees has greater power than selecting multiple cases from fewer pedigrees. Finally, we show how a pseudo-case-control design allows a greater range of statistical tests to be applied to family data.
Keywords: Rare variants; TDT; family-based association; missing heritability.
© 2014 The Authors. Annals of Human Genetics published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd/University College London.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Power of family-based association designs to detect rare variants in large pedigrees using imputed genotypes.Genet Epidemiol. 2014 Jan;38(1):1-9. doi: 10.1002/gepi.21776. Epub 2013 Nov 15. Genet Epidemiol. 2014. PMID: 24243664 Free PMC article.
-
The Rare-Variant Generalized Disequilibrium Test for Association Analysis of Nuclear and Extended Pedigrees with Application to Alzheimer Disease WGS Data.Am J Hum Genet. 2017 Feb 2;100(2):193-204. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2016.12.001. Epub 2017 Jan 5. Am J Hum Genet. 2017. PMID: 28065470 Free PMC article.
-
Increasing Generality and Power of Rare-Variant Tests by Utilizing Extended Pedigrees.Am J Hum Genet. 2016 Oct 6;99(4):846-859. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2016.08.015. Epub 2016 Sep 22. Am J Hum Genet. 2016. PMID: 27666371 Free PMC article.
-
The relative power of family-based and case-control designs for linkage disequilibrium studies of complex human diseases I. DNA pooling.Genome Res. 1998 Dec;8(12):1273-88. doi: 10.1101/gr.8.12.1273. Genome Res. 1998. PMID: 9872982 Review.
-
Rare variant association analysis methods for complex traits.Annu Rev Genet. 2010;44:293-308. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-102209-163421. Annu Rev Genet. 2010. PMID: 21047260 Review.
Cited by
-
Rare genetic variation implicated in non-Hispanic white families with Alzheimer disease.Neurol Genet. 2018 Nov 21;4(6):e286. doi: 10.1212/NXG.0000000000000286. eCollection 2018 Dec. Neurol Genet. 2018. PMID: 30569016 Free PMC article.
-
An adaptive strategy for association analysis of common or rare variants using entropy theory.J Hum Genet. 2017 Aug;62(8):777-781. doi: 10.1038/jhg.2017.39. Epub 2017 Apr 6. J Hum Genet. 2017. PMID: 28381878 Free PMC article.
-
Whole genome sequencing of Caribbean Hispanic families with late-onset Alzheimer's disease.Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2018 Mar 13;5(4):406-417. doi: 10.1002/acn3.537. eCollection 2018 Apr. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2018. PMID: 29688227 Free PMC article.
-
Rare variant association analysis in case-parents studies by allowing for missing parental genotypes.BMC Genet. 2018 Jan 15;19(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s12863-018-0597-8. BMC Genet. 2018. PMID: 29334894 Free PMC article.
-
Detecting disease association with rare variants in case-parents studies.J Hum Genet. 2017 Apr;62(5):549-552. doi: 10.1038/jhg.2017.1. Epub 2017 Feb 2. J Hum Genet. 2017. PMID: 28148922
References
-
- Antoniou AC. Easton DF. Polygenic inheritance of breast cancer: Implications for design of association studies. Genet Epidemiol. 2003;3:190–202. - PubMed
-
- Cordell HJ. Properties of case/pseudocontrol analysis for genetic association studies: Effects of recombination, ascertainment, and multiple affected offspring. Genet Epidemiol. 2004;3:186–205. - PubMed
-
- Cordell HJ, Barratt BJ. Clayton DG. Case/pseudocontrol analysis in genetic association studies: A unified framework for detection of genotype and haplotype associations, gene-gene and gene-environment interactions, and parent-of-origin effects. Genet Epidemiol. 2004;3:167–185. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

