Gene duplication in an African cichlid adaptive radiation
- PMID: 24571567
- PMCID: PMC3944005
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-161
Gene duplication in an African cichlid adaptive radiation
Abstract
Background: Gene duplication is a source of evolutionary innovation and can contribute to the divergence of lineages; however, the relative importance of this process remains to be determined. The explosive divergence of the African cichlid adaptive radiations provides both a model for studying the general role of gene duplication in the divergence of lineages and also an exciting foray into the identification of genomic features that underlie the dramatic phenotypic and ecological diversification in this particular lineage. We present the first genome-wide study of gene duplication in African cichlid fishes, identifying gene duplicates in three species belonging to the Lake Malawi adaptive radiation (Metriaclima estherae, Protomelas similis, Rhamphochromis "chilingali") and one closely related species from a non-radiated riverine lineage (Astatotilapia tweddlei).
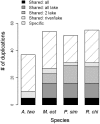
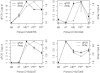
Results: Using Astatotilapia burtoni as reference, microarray comparative genomic hybridization analysis of 5689 genes reveals 134 duplicated genes among the four cichlid species tested. Between 51 and 55 genes were identified as duplicated in each of the three species from the Lake Malawi radiation, representing a 38%-49% increase in number of duplicated genes relative to the non-radiated lineage (37 genes). Duplicated genes include several that are involved in immune response, ATP metabolism and detoxification.
Conclusions: These results contribute to our understanding of the abundance and type of gene duplicates present in cichlid fish lineages. The duplicated genes identified in this study provide candidates for the analysis of functional relevance with regard to phenotype and divergence. Comparative sequence analysis of gene duplicates can address the role of positive selection and adaptive evolution by gene duplication, while further study across the phylogenetic range of cichlid radiations (and more generally in other adaptive radiations) will determine whether the patterns of gene duplication seen in this study consistently accompany rapid radiation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ancestral Hybridization Facilitated Species Diversification in the Lake Malawi Cichlid Fish Adaptive Radiation.Mol Biol Evol. 2020 Apr 1;37(4):1100-1113. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msz294. Mol Biol Evol. 2020. PMID: 31821500 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of prohormones and pituitary neuropeptides in the African cichlid, Astatotilapia burtoni.BMC Genomics. 2016 Aug 19;17(1):660. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2914-9. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27543050 Free PMC article.
-
The genomic substrate for adaptive radiation in African cichlid fish.Nature. 2014 Sep 18;513(7518):375-381. doi: 10.1038/nature13726. Epub 2014 Sep 3. Nature. 2014. PMID: 25186727 Free PMC article.
-
The evolutionary genomics of cichlid fishes: explosive speciation and adaptation in the postgenomic era.Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2014;15:417-41. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genom-090413-025412. Epub 2014 May 29. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2014. PMID: 24898042 Review.
-
African cichlid fish: a model system in adaptive radiation research.Proc Biol Sci. 2006 Aug 22;273(1597):1987-98. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2006.3539. Proc Biol Sci. 2006. PMID: 16846905 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Genomic Substrate for Adaptive Radiation: Copy Number Variation across 12 Tribes of African Cichlid Species.Genome Biol Evol. 2019 Oct 1;11(10):2856-2874. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evz185. Genome Biol Evol. 2019. PMID: 31504491 Free PMC article.
-
Correspondence of aCGH and long-read genome assembly for detection of copy number differences: A proof-of-concept with cichlid genomes.PLoS One. 2021 Oct 7;16(10):e0258193. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0258193. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34618847 Free PMC article.
-
Madagascar ground gecko genome analysis characterizes asymmetric fates of duplicated genes.BMC Biol. 2018 Apr 16;16(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s12915-018-0509-4. BMC Biol. 2018. PMID: 29661185 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the Function and Evolution of Taste 1 Receptor Gene Family in the Carnivore Fish Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata).Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 19;21(20):7732. doi: 10.3390/ijms21207732. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33086689 Free PMC article.
-
Copy number increases of transposable elements and protein-coding genes in an invasive fish of hybrid origin.Mol Ecol. 2017 Sep;26(18):4712-4724. doi: 10.1111/mec.14134. Epub 2017 Apr 28. Mol Ecol. 2017. PMID: 28390096 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dobzhansky T. Genetics of the evolutionary process. New York: Columbia University Press; 1937.
-
- Mayr E. Animal species and evolution. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Belknap Press of Harvard University Press; 1963.
-
- Schluter D. The Ecology of Adaptive Radiation. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press; 2000.
-
- Slatkin M. Ecological Character Displacement. Ecology. 1980;61:163–177. doi: 10.2307/1937166. - DOI
-
- Smith JM. Sympatric speciation. Am Nat. 1966;100:637. doi: 10.1086/282457. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

