Currarino syndrome in an adult presenting with a presacral abscess: a case report
- PMID: 24571710
- PMCID: PMC4234930
- DOI: 10.1186/1752-1947-8-77
Currarino syndrome in an adult presenting with a presacral abscess: a case report
Abstract
Introduction: Currarino syndrome (Currarino triad) was described in 1981 as a triad syndrome with a common embryogenesis in infants and with three characteristics: anorectal stenosis, a defect in the sacral bone, and a presacral mass. We describe here an unusual case of Currarino syndrome in an adult presenting with a presacral abscess but no meningitis.
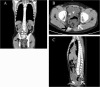
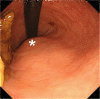
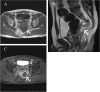
Case presentation: A 32-year-old Japanese man presented with fever, arthralgia and buttock pain. A digital rectal examination showed mild rectal stenosis with local warmth and tenderness in the posterior wall of his rectum. Computed tomography showed a scimitar-shaped deformity of his sacrum and an 8cm presacral mass, which continued to a pedicle of his deformed sacrum. This was diagnosed as Currarino syndrome with a presacral abscess. The abscess was drained by a perianal approach with our patient treated with antibiotics. His symptoms soon disappeared. After three months, an excision was performed through a posterior sagittal approach. His postoperative course was uneventful and he was discharged 10 days after surgery. A histopathological examination revealed an infected epidermoid cyst. He has been free from recurrence as of four years and six months after surgery.
Conclusions: We report a case of Currarino syndrome in an adult who presented with a presacral abscess but no meningitis. Abscess drainage followed by radical surgery resulted in a successful outcome.
Figures


References
-
- Ross AJ, Ruiz-Perez V, Wang Y, Hagan DM, Scherer S, Lynch SA, Lindsay S, Custard E, Belloni E, Wilson DI, Wadey R, Goodman F, Orstavik KH, Monclair T, Robson S, Reardon W, Burn J, Scambler P, Strachan T. A homeobox gene, HLXB9, is the major locus for dominantly inherited sacral agenesis. Nat Genet. 1998;20:358–361. doi: 10.1038/3828. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

