Magnetic heterogeneous catalytic ozonation: a new removal method for phenol in industrial wastewater
- PMID: 24572145
- PMCID: PMC3974053
- DOI: 10.1186/2052-336X-12-50
Magnetic heterogeneous catalytic ozonation: a new removal method for phenol in industrial wastewater
Abstract
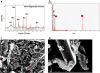
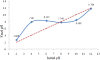
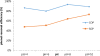
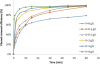
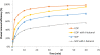
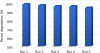
In this study, a new strategy in catalytic ozonation removal method for degradation of phenol from industrial wastewater was investigated. Magnetic carbon nano composite as a novel catalyst was synthesized, characterized and then used in the catalytic ozonation process (COP) and compared with the single ozonation process (SOP). The influential parameters were all investigated. The results showed that the removal efficiency of phenol and COD (chemical oxygen demand) in COP (98.5%, 69.8%) was higher than those of SOP (78.7%, 50.5%) and the highest catalytic potential was achieved at optimal neutral pH. First order modeling demonstrated that the reactions were dependent on the concentration of catalyst, with kinetic constants varying from 0.023 1/min (catalyst = 0 g/L) to 0.071 1/min (catalyst = 4 g/L), whereby the optimum dosage of catalyst was found to be 2 g/L. Furthermore, the catalytic properties of the catalyst remained almost unchanged after 5-time reuse. The results regarding the biodegradability of the effluent showed that a 5-min reaction time in COP reduced the concentrations of phenol and COD to the acceptable levels for the efficient post-treatment in the SBR in a 4-h cycle period. Finally, this combined system is proven to be a technically effective method for treating phenolic contaminants.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The investigation of catalytic ozonation and integrated catalytic ozonation/biological processes for the removal of phenol from saline wastewaters.J Hazard Mater. 2009 Nov 15;171(1-3):175-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.05.113. Epub 2009 Jun 6. J Hazard Mater. 2009. PMID: 19560265
-
Catalytic ozonation-biological coupled processes for the treatment of industrial wastewater containing refractory chlorinated nitroaromatic compounds.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2010 Mar;11(3):177-89. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B0900291. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2010. PMID: 20205304 Free PMC article.
-
Fe-zeolite catalyst for ozonation of pulp and paper wastewater for sustainable water resources.Chemosphere. 2022 Jun;297:134031. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134031. Epub 2022 Feb 18. Chemosphere. 2022. PMID: 35189191
-
Catalytic ozonation of phenol using copper coated pumice and zeolite as catalysts.J Res Health Sci. 2012 Dec 13;12(2):93-7. J Res Health Sci. 2012. PMID: 23241518
-
Catalytic ozonation of phenol by ZnFe2O4/ZnNCN: performance and mechanism.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022 Dec;29(58):88172-88181. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-21696-8. Epub 2022 Jul 13. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35831647
Cited by
-
A comparative study of anaerobic fixed film baffled reactor and up-flow anaerobic fixed film fixed bed reactor for biological removal of diethyl phthalate from wastewater: a performance, kinetic, biogas, and metabolic pathway study.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2017 May 31;10:139. doi: 10.1186/s13068-017-0826-9. eCollection 2017. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2017. PMID: 28580013 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Clay Minerals in Natural Media Self-Regeneration from Organic Pollution-Prospects for Nature-Inspired Water Treatments.Molecules. 2024 Oct 29;29(21):5108. doi: 10.3390/molecules29215108. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39519749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Removal of 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid from water and organic by-product minimization by catalytic ozonation.J Environ Health Sci Eng. 2018 Dec 17;17(1):85-95. doi: 10.1007/s40201-018-00329-8. eCollection 2019 Jun. J Environ Health Sci Eng. 2018. PMID: 31297204 Free PMC article.
-
The catalytic ozonation of diazinon using nano-MgO@CNT@Gr as a new heterogenous catalyst: the optimization of effective factors by response surface methodology.RSC Adv. 2020 Feb 21;10(13):7718-7731. doi: 10.1039/c9ra10095d. eCollection 2020 Feb 18. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35492203 Free PMC article.
-
Application of concrete surfaces as novel substrate for immobilization of TiO2 nano powder in photocatalytic treatment of phenolic water.J Environ Health Sci Eng. 2015 Aug 4;13:58. doi: 10.1186/s40201-015-0214-y. eCollection 2015. J Environ Health Sci Eng. 2015. PMID: 26244097 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chang C-C, Chiu C-Y, Chang C-Y, Chang C-F, Chen Y-H, Ji D-R, Tseng J-Y, Yu Y-H. Pt-catalyzed ozonation of aqueous phenol solution using high-gravity rotating packed bed. J Hazard Mater. 2009;168(2–3):649–655. - PubMed
-
- Aguinaco A, Beltrán FJ, García-Araya JF, Oropesa A. Photocatalytic ozonation to remove the pharmaceutical diclofenac from water: influence of variables. Chem Eng J. 2012;189–190:275–282. - PubMed
-
- Y-f R, H-j L, C-h W, L-f L. Catalytic ozonation of phenol and oxalic acid with copper-loaded activated carbon. J Central South Univ Technol. 2010;17(2):300–306. doi: 10.1007/s11771-010-0046-y. - DOI
-
- Pocostales P, Alvarez P, Beltran FJ. Catalytic ozonation promoted by alumina-based catalysts for the removal of some pharmaceutical compounds from water. Chem Eng J. 2011;168(3):1289–1295. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2011.02.042. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

