Splicing factor hnRNP A2 activates the Ras-MAPK-ERK pathway by controlling A-Raf splicing in hepatocellular carcinoma development
- PMID: 24572810
- PMCID: PMC3964912
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.042259.113
Splicing factor hnRNP A2 activates the Ras-MAPK-ERK pathway by controlling A-Raf splicing in hepatocellular carcinoma development
Abstract
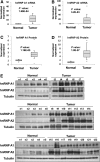
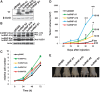
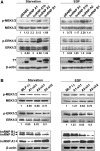
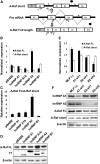
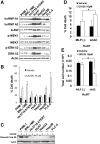
In recent years, it has become clear that splicing factors play a direct role in cancer development. We showed previously that splicing factors SRSF1, SRSF6, and hnRNP A2/B1 are up-regulated in several cancers and can act as oncogenes when up-regulated. Here we examined the role of splicing factors hnRNP A1/A1b and hnRNP A2/B1 in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). We show that the splicing factors hnRNP A1 and hnRNP A2 are up-regulated in HCC tumors derived from inflammation-induced liver cancer mouse model. Overexpression of hnRNP A1 or hnRNP A2, but not the splicing isoform hnRNP B1, induced tumor formation of immortalized liver progenitor cells, while knockdown of these proteins inhibited anchorage-independent growth and tumor growth of human liver cancer cell lines. In addition, we found that cells overexpressing hnRNP A2 showed constitutive activation of the Ras-MAPK-ERK pathway. In contrast, knockdown of hnRNP A2 inhibited the Ras-MAPK-ERK pathway and prevented ERK1/2 activation by EGF. Moreover, we found that hnRNP A2 regulates the splicing of A-Raf, reducing the production of a short dominant-negative isoform of A-Raf and elevating the full-length A-Raf transcript. Taken together, our data suggest that hnRNP A2 up-regulation in HCC induces an alternative splicing switch that down-regulates a dominant-negative isoform of A-Raf, leading to activation of the Raf-MEK-ERK pathway and cellular transformation.
Keywords: A-Raf; MAPK; RNA processing; alternative splicing; hnRNP A2/B1; liver cancer.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Up-regulation and subcellular localization of hnRNP A2/B1 in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2010 Jul 6;10:356. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-356. BMC Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20604928 Free PMC article.
-
Protein kinase C alpha trigger Ras and Raf-independent MEK/ERK activation for TPA-induced growth inhibition of human hepatoma cell HepG2.Cancer Lett. 2006 Jul 28;239(1):27-35. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2005.07.034. Epub 2005 Sep 19. Cancer Lett. 2006. PMID: 16169661
-
HnRNP A1/A2 and SF2/ASF regulate alternative splicing of interferon regulatory factor-3 and affect immunomodulatory functions in human non-small cell lung cancer cells.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 29;8(4):e62729. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062729. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23658645 Free PMC article.
-
Dominant-negative antagonists of the Ras-ERK pathway: DA-Raf and its related proteins generated by alternative splicing of Raf.Exp Cell Res. 2020 Feb 15;387(2):111775. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2019.111775. Epub 2019 Dec 13. Exp Cell Res. 2020. PMID: 31843497 Review.
-
The Ras/MAPK pathway and hepatocarcinoma: pathogenesis and therapeutic implications.Eur J Clin Invest. 2015 Jun;45(6):609-23. doi: 10.1111/eci.12441. Epub 2015 May 11. Eur J Clin Invest. 2015. PMID: 25832714 Review.
Cited by
-
Inflammatory Microenvironment Modulation of Alternative Splicing in Cancer: A Way to Adapt.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1219:243-258. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-34025-4_13. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32130703 Review.
-
Differential localization of A-Raf regulates MST2-mediated apoptosis during epithelial differentiation.Cell Death Differ. 2016 Aug;23(8):1283-95. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2016.2. Epub 2016 Feb 19. Cell Death Differ. 2016. PMID: 26891695 Free PMC article.
-
How Driver Oncogenes Shape and Are Shaped by Alternative Splicing Mechanisms in Tumors.Cancers (Basel). 2023 May 26;15(11):2918. doi: 10.3390/cancers15112918. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37296881 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular targets and mechanisms of different aberrant alternative splicing in metastatic liver cancer.World J Clin Oncol. 2024 Apr 24;15(4):531-539. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v15.i4.531. World J Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38689626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multivalent Molecules as Modulators of RNA Granule Size and Composition.Biophys J. 2017 Jul 25;113(2):235-245. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2017.01.031. Epub 2017 Feb 24. Biophys J. 2017. PMID: 28242011 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
