Distinct functional classes of ram mutations in 16S rRNA
- PMID: 24572811
- PMCID: PMC3964911
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.043331.113
Distinct functional classes of ram mutations in 16S rRNA
Abstract
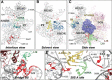
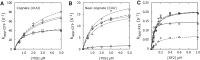
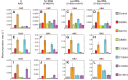
During decoding, the ribosome selects the correct (cognate) aminoacyl-tRNA (aa-tRNA) from a large pool of incorrect aa-tRNAs through a two-stage mechanism. In the initial selection stage, aa-tRNA is delivered to the ribosome as part of a ternary complex with elongation factor EF-Tu and GTP. Interactions between codon and anticodon lead to activation of the GTPase domain of EF-Tu and GTP hydrolysis. Then, in the proofreading stage, aa-tRNA is released from EF-Tu and either moves fully into the A/A site (a step termed "accommodation") or dissociates from the ribosome. Cognate codon-anticodon pairing not only stabilizes aa-tRNA at both stages of decoding but also stimulates GTP hydrolysis and accommodation, allowing the process to be both accurate and fast. In previous work, we isolated a number of ribosomal ambiguity (ram) mutations in 16S rRNA, implicating particular regions of the ribosome in the mechanism of decoding. Here, we analyze a representative subset of these mutations with respect to initial selection, proofreading, RF2-dependent termination, and overall miscoding in various contexts. We find that mutations that disrupt inter-subunit bridge B8 increase miscoding in a general way, causing defects in both initial selection and proofreading. Mutations in or near the A site behave differently, increasing miscoding in a codon-anticodon-dependent manner. These latter mutations may create spurious favorable interactions in the A site for certain near-cognate aa-tRNAs, providing an explanation for their context-dependent phenotypes in the cell.
Keywords: EF-Tu; decoding; ribosome; tRNA; translation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ensemble cryo-EM elucidates the mechanism of translation fidelity.Nature. 2017 Jun 1;546(7656):113-117. doi: 10.1038/nature22397. Epub 2017 May 24. Nature. 2017. PMID: 28538735 Free PMC article.
-
Structural dynamics of translation elongation factor Tu during aa-tRNA delivery to the ribosome.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Sep 19;46(16):8651-8661. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky651. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 30107527 Free PMC article.
-
Elongation factor-Tu can repetitively engage aminoacyl-tRNA within the ribosome during the proofreading stage of tRNA selection.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Feb 18;117(7):3610-3620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1904469117. Epub 2020 Feb 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32024753 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple stages in codon-anticodon recognition: double-trigger mechanisms and geometric constraints.Biochimie. 2006 Aug;88(8):963-92. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2006.06.002. Epub 2006 Jun 27. Biochimie. 2006. PMID: 16843583 Review.
-
Structural dynamics of ribosomal RNA during decoding on the ribosome.Biochimie. 2002 Aug;84(8):745-54. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(02)01409-8. Biochimie. 2002. PMID: 12457562 Review.
Cited by
-
Fail-safe genetic codes designed to intrinsically contain engineered organisms.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Nov 4;47(19):10439-10451. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz745. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 31511890 Free PMC article.
-
Intersubunit Bridges of the Bacterial Ribosome.J Mol Biol. 2016 May 22;428(10 Pt B):2146-64. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2016.02.009. Epub 2016 Feb 13. J Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26880335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of decoding fidelity by ribosomal proteins S4 and S5.J Bacteriol. 2015 Mar;197(6):1017-25. doi: 10.1128/JB.02485-14. Epub 2014 Dec 29. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 25548247 Free PMC article.
-
Evolving Mistranslating tRNAs Through a Phenotypically Ambivalent Intermediate in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2017 Aug;206(4):1865-1879. doi: 10.1534/genetics.117.203232. Epub 2017 Jun 2. Genetics. 2017. PMID: 28576863 Free PMC article.
-
Atomic mutagenesis at the ribosomal decoding site.RNA Biol. 2017 Jan 2;14(1):104-112. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2016.1256535. Epub 2016 Nov 14. RNA Biol. 2017. PMID: 27841727 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arkov AL, Freistroffer DV, Pavlov MY, Ehrenberg M, Murgola EJ 2000. Mutations in conserved regions of ribosomal RNAs decrease the productive association of peptide-chain release factors with the ribosome during translation termination. Biochimie 82: 671–682 - PubMed
-
- Bjorkman J, Samuelsson P, Andersson DI, Hughes D 1999. Novel ribosomal mutations affecting translational accuracy, antibiotic resistance and virulence of Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Microbiol 31: 53–58 - PubMed
-
- Cannone JJ, Subramanian S, Schnare MN, Collett JR, D’Souza LM, Du Y, Feng B, Lin N, Madabusi LV, Muller KM, et al. 2002. The comparative RNA web (CRW) site: An online database of comparative sequence and structure information for ribosomal, intron, and other RNAs. BMC Bioinformatics 3: 2. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carter AP, Clemons WM, Brodersen DE, Morgan-Warren RJ, Wimberly BT, Ramakrishnan V 2000. Functional insights from the structure of the 30S ribosomal subunit and its interactions with antibiotics. Nature 407: 340–348 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
