Remembering to eat: hippocampal regulation of meal onset
- PMID: 24573183
- PMCID: PMC4025066
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00496.2013
Remembering to eat: hippocampal regulation of meal onset
Abstract
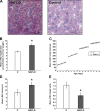
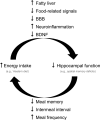
A wide variety of species, including vertebrate and invertebrates, consume food in bouts (i.e., meals). Decades of research suggest that different mechanisms regulate meal initiation (when to start eating) versus meal termination (how much to eat in a meal, also known as satiety). There is a very limited understanding of the mechanisms that regulate meal onset and the duration of the postprandial intermeal interval (ppIMI). In the present review, we examine issues involved in measuring meal onset and some of the limited available evidence regarding how it is regulated. Then, we describe our recent work indicating that dorsal hippocampal neurons inhibit meal onset during the ppIMI and describe the processes that may be involved in this. We also synthesize recent evidence, including evidence from our laboratory, suggesting that overeating impairs hippocampal functioning and that impaired hippocampal functioning, in turn, contributes to the development and/or maintenance of diet-induced obesity. Finally, we identify critical questions and challenges for future research investigating neural controls of meal onset.
Keywords: energy intake; hippocampus; meal onset; memory; obesity.
Copyright © 2014 the American Physiological Society.
Figures
References
-
- Acosta GB. A possible interaction between CCKergic and GABAergic systems in the rat brain. Comp Biochem Physiol Toxicol Pharmacol 128: 11–17, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Alzoubi KH, Khabour OF, Salah HA, Abu Rashid BE. The combined effect of sleep deprivation and Western diet on spatial learning and memory: role of BDNF and oxidative stress. J Mol Neurosci 50: 124–133, 2013 - PubMed
-
- Alzoubi KH, Khabour OF, Salah HA, Hasan Z. Vitamin E prevents high-fat high-carbohydrates diet-induced memory impairment: the role of oxidative stress. Physiol Behav 119: 72–78, 2013 - PubMed
-
- Amaral DG, Insausti R, Cowan WM. The entorhinal cortex of the monkey: I. Cytoarchitectonic organization. J Comp Neurol 264: 326–355, 1987 - PubMed
-
- Antin J, Gibbs J, Holt J, Young RC, Smith GP. Cholecystokinin elicits the complete behavioral sequence of satiety in rats. J Comp Physiol Psychol 89: 784–790, 1975 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

