Sensor network infrastructure for a home care monitoring system
- PMID: 24573309
- PMCID: PMC4003918
- DOI: 10.3390/s140303833
Sensor network infrastructure for a home care monitoring system
Abstract
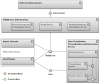
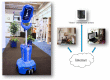
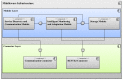
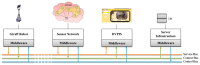
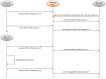
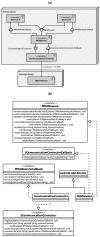
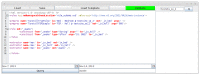
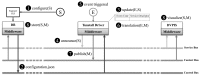
This paper presents the sensor network infrastructure for a home care system that allows long-term monitoring of physiological data and everyday activities. The aim of the proposed system is to allow the elderly to live longer in their home without compromising safety and ensuring the detection of health problems. The system offers the possibility of a virtual visit via a teleoperated robot. During the visit, physiological data and activities occurring during a period of time can be discussed. These data are collected from physiological sensors (e.g., temperature, blood pressure, glucose) and environmental sensors (e.g., motion, bed/chair occupancy, electrical usage). The system can also give alarms if sudden problems occur, like a fall, and warnings based on more long-term trends, such as the deterioration of health being detected. It has been implemented and tested in a test environment and has been deployed in six real homes for a year-long evaluation. The key contribution of the paper is the presentation of an implemented system for ambient assisted living (AAL) tested in a real environment, combining the acquisition of sensor data, a flexible and adaptable middleware compliant with the OSGistandard and a context recognition application. The system has been developed in a European project called GiraffPlus.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A system for ubiquitous fall monitoring at home via a wireless sensor network.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2010;2010:2246-9. doi: 10.1109/IEMBS.2010.5627338. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2010. PMID: 21096580
-
Multimodal wireless sensor network-based ambient assisted living in real homes with multiple residents.Sensors (Basel). 2014 May 30;14(6):9692-719. doi: 10.3390/s140609692. Sensors (Basel). 2014. PMID: 24887044 Free PMC article.
-
Wireless-accessible sensor populations for monitoring biological variables.J Telemed Telecare. 2008;14(3):135-7. doi: 10.1258/jtt.2008.003010. J Telemed Telecare. 2008. PMID: 18430280
-
Sensor technology for smart homes.Maturitas. 2011 Jun;69(2):131-6. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2011.03.016. Epub 2011 May 4. Maturitas. 2011. PMID: 21531517 Review.
-
Ambient Sensors for Elderly Care and Independent Living: A Survey.Sensors (Basel). 2018 Jun 25;18(7):2027. doi: 10.3390/s18072027. Sensors (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29941804 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Assistant Personal Robot (APR): Conception and Application of a Tele-Operated Assisted Living Robot.Sensors (Basel). 2016 Apr 28;16(5):610. doi: 10.3390/s16050610. Sensors (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27136552 Free PMC article.
-
Experiences With Developing and Using Vital Sign Telemonitoring to Support Mobile Nursing in Rural Regions: Feasibility and Usability Study.JMIR Nurs. 2020 Apr 23;3(1):e17113. doi: 10.2196/17113. eCollection 2020 Jan-Dec. JMIR Nurs. 2020. PMID: 34345782 Free PMC article.
-
A Real-Time Health Monitoring System for Remote Cardiac Patients Using Smartphone and Wearable Sensors.Int J Telemed Appl. 2015;2015:373474. doi: 10.1155/2015/373474. Epub 2015 Dec 15. Int J Telemed Appl. 2015. PMID: 26788055 Free PMC article.
-
Technological Ecosystems in Care and Assistance: A Systematic Literature Review.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Feb 9;19(3):708. doi: 10.3390/s19030708. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30744096 Free PMC article.
-
Distributed service-based approach for sensor data fusion in IoT environments.Sensors (Basel). 2014 Oct 15;14(10):19200-28. doi: 10.3390/s141019200. Sensors (Basel). 2014. PMID: 25320907 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bonato P. Wearable Sensors and Systems. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 2010;29:25–36. - PubMed
-
- Lymberis A., Paradiso R. Smart Fabrics and Interactive Textile Enabling Wearable Personal Applications: R&D State of the Art and future Challenges. Proceedings of 30th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBS 2008); Vancouver, Canada. 19 April 2008; pp. 5270–5273. - PubMed
-
- Wartena F., Muskens J., Schmitt L., Petkovic M. Continua: The Reference Architecture of a Personal Telehealth Ecosystem. Proceedings of 12th IEEE International Conference on e-Health Networking Applications and Services (Healthcom); Lyon, France. 1–3 July 2010; pp. 1–6.
-
- Schmitt L., Falck T., Wartena F., Simons D. Novel ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards for Personal Telehealth Systems Interoperability. Proceedings of IEEE Workshop on High Confidence Medical Devices, Software, and Systems and Medical Device Plug-and-Play Interoperability (HCMDSS-MDPn); Boston, MA, USA. 25–27 June 2007; pp. 146–148.
-
- Amoretti M., Wientapper F., Furfari F., Lenzi S., Chessa S. Sensor Systems and Software. Springer; Pisa, Italy: 2010. Sensor Data Fusion for Activity Monitoring in Ambient Assisted Living Environments; pp. 206–221.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

