Temporal trends in ischemic heart disease mortality in 21 world regions, 1980 to 2010: the Global Burden of Disease 2010 study
- PMID: 24573352
- PMCID: PMC4181359
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.004042
Temporal trends in ischemic heart disease mortality in 21 world regions, 1980 to 2010: the Global Burden of Disease 2010 study
Abstract
Background: Ischemic heart disease (IHD) is the leading cause of death worldwide. The Global Burden of Diseases, Risk Factors and Injuries 2010 Study estimated global and regional IHD mortality from 1980 to 2010.
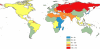
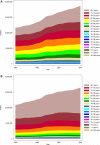
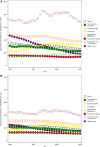
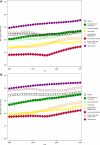
Methods and results: Sources for IHD mortality estimates were country-level surveillance, verbal autopsy, and vital registration data. Regional income, metabolic and nutritional risk factors, and other covariates were estimated from surveys and a systematic review. An estimation and validation process led to an ensemble model of IHD mortality for 21 world regions. Globally, age-standardized IHD mortality has declined since the 1980s, and high-income regions (especially Australasia, Western Europe, and North America) experienced the most remarkable declines. Age-standardized IHD mortality increased in former Soviet Union countries and South Asia in the 1990s and attenuated after 2000. In 2010, Eastern Europe and Central Asia had the highest age-standardized IHD mortality rates. More IHD deaths occurred in South Asia in 2010 than in any other region. On average, IHD deaths in South Asia, North Africa and the Middle East, and sub-Saharan Africa occurred at younger ages in comparison with most other regions.
Conclusions: In most world regions, particularly in high-income regions, age-standardized IHD mortality rates have declined significantly since 1980. High age-standardized IHD mortality in Eastern Europe, Central Asia, and South Asia point to the need to prevent and control established risk factors in those regions and to research the unique behavioral and environmental determinants of higher IHD mortality.
Keywords: epidemiology; mortality; myocardial ischemia; trends; world health.
Figures
Comment in
-
Documenting the global burden of cardiovascular disease: a major achievement but still a work in progress.Circulation. 2014 Apr 8;129(14):1459-62. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.008302. Epub 2014 Feb 26. Circulation. 2014. PMID: 24573353 No abstract available.
-
Public health. Quantifying the global burden of ischaemic heart disease.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2014 May;11(5):248. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2014.31. Epub 2014 Mar 18. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 24642647 No abstract available.
References
-
- Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S, Shibuya K, Aboyans V, Abraham J, Adair T, Aggarwal R, Ahn SY, Alvarado M, Anderson HR, Anderson LM, Andrews KG, Atkinson C, Baddour LM, Barker-Collo S, Bartels DH, Bell ML, Benjamin EJ, Bennett D, Bhalla K, Bikbov B, Bin Abdulhak A, Birbeck G, Blyth F, Bolliger I, Boufous S, Bucello C, Burch M, Burney P, Carapetis J, Chen H, Chou D, Chugh SS, Coffeng LE, Colan SD, Colquhoun S, Colson KE, Condon J, Connor MD, Cooper LT, Corriere M, Cortinovis M, de Vaccaro KC, Couser W, Cowie BC, Criqui MH, Cross M, Dabhadkar KC, Dahodwala N, De Leo D, Degenhardt L, Delossantos A, Denenberg J, Des Jarlais DC, Dharmaratne SD, Dorsey ER, Driscoll T, Duber H, Ebel B, Erwin PJ, Espindola P, Ezzati M, Feigin V, Flaxman AD, Forouzanfar MH, Fowkes FG, Franklin R, Fransen M, Freeman MK, Gabriel SE, Gakidou E, Gaspari F, Gillum RF, Gonzalez-Medina D, Halasa YA, Haring D, Harrison JE, Havmoeller R, Hay RJ, Hoen B, Hotez PJ, Hoy D, Jacobsen KH, James SL, Jasrasaria R, Jayaraman S, Johns N, Karthikeyan G, Kassebaum N, Keren A, Khoo JP, Knowlton LM, Kobusingye O, Koranteng A, Krishnamurthi R, Lipnick M, Lipshultz SE, Ohno SL, Mabweijano J, MacIntyre MF, Mallinger L, March L, Marks GB, Marks R, Matsumori A, Matzopoulos R, Mayosi BM, McAnulty JH, McDermott MM, McGrath J, Mensah GA, Merriman TR, Michaud C, Miller M, Miller TR, Mock C, Mocumbi AO, Mokdad AA, Moran A, Mulholland K, Nair MN, Naldi L, Narayan KM, Nasseri K, Norman P, O'Donnell M, Omer SB, Ortblad K, Osborne R, Ozgediz D, Pahari B, Pandian JD, Rivero AP, Padilla RP, Perez-Ruiz F, Perico N, Phillips D, Pierce K, Pope CA, 3rd, Porrini E, Pourmalek F, Raju M, Ranganathan D, Rehm JT, Rein DB, Remuzzi G, Rivara FP, Roberts T, De León FR, Rosenfeld LC, Rushton L, Sacco RL, Salomon JA, Sampson U, Sanman E, Schwebel DC, Segui-Gomez M, Shepard DS, Singh D, Singleton J, Sliwa K, Smith E, Steer A, Taylor JA, Thomas B, Tleyjeh IM, Towbin JA, Truelsen T, Undurraga EA, Venketasubramanian N, Vijayakumar L, Vos T, Wagner GR, Wang M, Wang W, Watt K, Weinstock MA, Weintraub R, Wilkinson JD, Woolf AD, Wulf S, Yeh PH, Yip P, Zabetian A, Zheng ZJ, Lopez AD, Murray CJ, AlMazroa MA, Memish ZA. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380:2095–2128. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tunstall-Pedoe H, Vanuzzo D, Hobbs M, Mähönen M, Cepaitis Z, Kuulasmaa K, Keil U. Estimation of contribution of changes in coronary care to improving survival, event rates, and coronary heart disease mortality across the WHO MONICA Project populations. Lancet. 2000;355:688–700. - PubMed
-
- Kuulasmaa K, Tunstall-Pedoe H, Dobson A, Fortmann S, Sans S, Tolonen H, Evans A, Ferrario M, Tuomilehto J. Estimation of contribution of changes in classic risk factors to trends in coronary-event rates across the WHO MONICA Project populations. Lancet. 2000;355:675–687. - PubMed
-
- Ford ES, Ajani UA, Croft JB, Critchley JA, Labarthe DR, Kottke TE, Giles WH, Capewell S. Explaining the decrease in U.S. deaths from coronary disease, 1980-2000. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:2388–2398. - PubMed
-
- Di Cesare M, Bennett JE, Best N, Stevens GA, Danaei G, Ezzati M. The contributions of risk factor trends to cardiometabolic mortality decline in industrialized countries. Int J Epidemiol. 2013;42:838–848. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

