Insight into the roles of helicase motif Ia by characterizing Fanconi anemia group J protein (FANCJ) patient mutations
- PMID: 24573678
- PMCID: PMC4036176
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.538892
Insight into the roles of helicase motif Ia by characterizing Fanconi anemia group J protein (FANCJ) patient mutations
Abstract
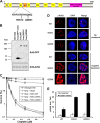
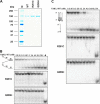
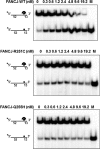
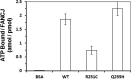
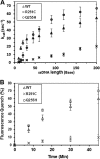
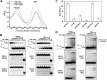
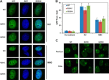
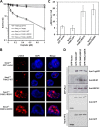
Helicases are molecular motors that couple the energy of ATP hydrolysis to the unwinding and remodeling of structured DNA or RNA, which is coordinated by conserved helicase motifs. FANCJ is a DNA helicase that is genetically linked to Fanconi anemia, breast cancer, and ovarian cancer. Here, we characterized two Fanconi anemia patient mutations, R251C and Q255H, that are localized in helicase motif Ia. Our genetic complementation analysis revealed that both the R251C and Q255H alleles failed to rescue cisplatin sensitivity of a FANCJ null cell line as detected by cell survival or γ-H2AX foci formation. Furthermore, our biochemical assays demonstrated that both purified recombinant proteins abolished DNA helicase activity and failed to disrupt the DNA-protein complex. Intriguingly, R251C impaired DNA binding ability to single-strand DNA and double-strand DNA, whereas Q255H retained higher binding activity to these DNA substrates compared with wild-type FANCJ protein. Consequently, R251C abolished its DNA-dependent ATP hydrolysis activity, whereas Q255H retained normal ATPase activity. Physically, R251C had reduced ATP binding ability, whereas Q255H had normal ATP binding ability and could translocate on single-strand DNA. Although both proteins were recruited to damage sites in our laser-activated confocal assays, they lost their DNA repair function, which explains why they exerted a domain negative effect when expressed in a wild-type background. Taken together, our work not only reveals the structural function of helicase motif Ia but also provides the molecular pathology of FANCJ in related diseases.
Keywords: DNA Helicase; DNA Repair; Enzymes; FANCJ; Fanconi Anemia; Helicase; Motif Ia; Mutant; Pathogenesis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Q motif of Fanconi anemia group J protein (FANCJ) DNA helicase regulates its dimerization, DNA binding, and DNA repair function.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jun 22;287(26):21699-716. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.351338. Epub 2012 May 10. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22582397 Free PMC article.
-
Fanconi anemia group J mutation abolishes its DNA repair function by uncoupling DNA translocation from helicase activity or disruption of protein-DNA complexes.Blood. 2010 Nov 11;116(19):3780-91. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-11-256016. Epub 2010 Jul 16. Blood. 2010. PMID: 20639400 Free PMC article.
-
A minimal threshold of FANCJ helicase activity is required for its response to replication stress or double-strand break repair.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jul 6;46(12):6238-6256. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky403. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29788478 Free PMC article.
-
Mutational analysis of FANCJ helicase.Methods. 2016 Oct 1;108:118-29. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2016.04.023. Epub 2016 Apr 21. Methods. 2016. PMID: 27107905 Review.
-
FANCJ helicase operates in the Fanconi Anemia DNA repair pathway and the response to replicational stress.Curr Mol Med. 2009 May;9(4):470-82. doi: 10.2174/156652409788167159. Curr Mol Med. 2009. PMID: 19519404 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The DEAD-box protein DDX43 (HAGE) is a dual RNA-DNA helicase and has a K-homology domain required for full nucleic acid unwinding activity.J Biol Chem. 2017 Jun 23;292(25):10429-10443. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.774950. Epub 2017 May 3. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28468824 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and cellular functions of the FANCJ DNA helicase defective in cancer and in Fanconi anemia.Front Genet. 2014 Oct 21;5:372. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00372. eCollection 2014. Front Genet. 2014. PMID: 25374583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Loss of Mitochondrial Localization of Human FANCG Causes Defective FANCJ Helicase.Mol Cell Biol. 2020 Nov 6;40(23):e00306-20. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00306-20. Print 2020 Nov 6. Mol Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32989015 Free PMC article.
-
Update of the human and mouse Fanconi anemia genes.Hum Genomics. 2015 Nov 24;9:32. doi: 10.1186/s40246-015-0054-y. Hum Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26596371 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Helicase-inactivating BRIP1 mutation yields Fanconi anemia with microcephaly and other congenital abnormalities.Cold Spring Harb Mol Case Stud. 2020 Oct 7;6(5):a005652. doi: 10.1101/mcs.a005652. Print 2020 Oct. Cold Spring Harb Mol Case Stud. 2020. PMID: 33028645 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dillingham M. S. (2011) Superfamily I helicases as modular components of DNA-processing machines. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 39, 413–423 - PubMed
-
- Lohman T. M., Bjornson K. P. (1996) Mechanisms of helicase-catalyzed DNA unwinding. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 65, 169–214 - PubMed
-
- Lohman T. M., Tomko E. J., Wu C. G. (2008) Non-hexameric DNA helicases and translocases. Mechanisms and regulation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 9, 391–401 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

