In vivo genome-wide binding of Id2 to E2F4 target genes as part of a reversible program in mice liver
- PMID: 24573694
- PMCID: PMC11113549
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-014-1588-1
In vivo genome-wide binding of Id2 to E2F4 target genes as part of a reversible program in mice liver
Abstract
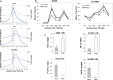
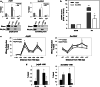
The inhibitor of differentiation Id2, a protein lacking the basic DNA-binding domain, is involved in the modulation of a number of biological processes. The molecular mechanisms explaining Id2 pleiotropic functions are poorly understood. Id2 and E2F4 are known to bind simultaneously to c-myc promoter. To study whether Id2 plays a global role on transcriptional regulation, we performed in vivo genome-wide ChIP/chip experiments for Id2 and E2F4 in adult mouse liver. An Id2-containing complex was bound to a common sequence downstream from the TSS on a subset of 442 E2F4 target genes mainly related to cell development and chromatin structure. We found a positive correlation between Id2 protein levels and the expression of E2F4/Id2 targets in fetal and adult liver. Id2 protein stability increased in fetal liver by interaction with USP1 de-ubiquitinating enzyme, which was induced during development. In adult liver, USP1 and Id2 levels dramatically decreased. In differentiated liver tissue, when Id2 concentration was low, E2F4/Id2 was bound to the same region as paused Pol II and target genes remained transcriptionally inactive. Conversely, in fetal liver when Id2 levels were increased, Id2 and Pol II were released from gene promoters and target genes up-regulated. During liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy, we obtained the same results as in fetal liver. Our results suggest that Id2 might be part of a reversible development-related program involved in the paused-ON/OFF state of Pol II on selected genes that would remain responsive to specific stimuli.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Id2 leaves the chromatin of the E2F4-p130-controlled c-myc promoter during hepatocyte priming for liver regeneration.Biochem J. 2006 Sep 15;398(3):431-7. doi: 10.1042/BJ20060380. Biochem J. 2006. PMID: 16776654 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms of Id2 down-regulation in rat liver after acetaminophen overdose. Protection by N-acetyl-L-cysteine.Free Radic Res. 2010 Sep;44(9):1044-53. doi: 10.3109/10715762.2010.498825. Free Radic Res. 2010. PMID: 20815767
-
Temporal ChIP-on-Chip of RNA-Polymerase-II to detect novel gene activation events during photoreceptor maturation.Mol Vis. 2010 Feb 17;16:252-71. Mol Vis. 2010. PMID: 20161818 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between NRF1, E2F4 and MYC transcription factors regulating common target genes contributes to cancer development and progression.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2018 Oct;41(5):465-484. doi: 10.1007/s13402-018-0395-3. Epub 2018 Jul 25. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2018. PMID: 30047092 Review.
-
Novel functions for the transcription factor E2F4 in development and disease.Cell Cycle. 2016 Dec;15(23):3183-3190. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2016.1234551. Epub 2016 Oct 18. Cell Cycle. 2016. PMID: 27753528 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cellular Id1 inhibits hepatitis B virus transcription by interacting with the novel covalently closed circular DNA-binding protein E2F4.Int J Biol Sci. 2022 Jan 1;18(1):65-81. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.62106. eCollection 2022. Int J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 34975318 Free PMC article.
-
E2F4 Promotes the Proliferation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells through Upregulation of CDCA3.J Cancer. 2021 Jun 22;12(17):5173-5180. doi: 10.7150/jca.53708. eCollection 2021. J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34335934 Free PMC article.
-
scCompass: An Integrated Multi-Species scRNA-seq Database for AI-Ready.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Jul;12(25):e2500870. doi: 10.1002/advs.202500870. Epub 2025 May 2. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 40317650 Free PMC article.
-
Sex Difference of Egfr Expression and Molecular Pathway in the Liver: Impact on Drug Design and Cancer Treatments?J Cancer. 2016 Mar 20;7(6):671-80. doi: 10.7150/jca.13684. eCollection 2016. J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27076848 Free PMC article.
-
Early developmental gene enhancers affect subcortical volumes in the adult human brain.Hum Brain Mapp. 2016 May;37(5):1788-800. doi: 10.1002/hbm.23136. Epub 2016 Feb 18. Hum Brain Mapp. 2016. PMID: 26890892 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

