TSLP signaling pathway map: a platform for analysis of TSLP-mediated signaling
- PMID: 24573880
- PMCID: PMC3935308
- DOI: 10.1093/database/bau007
TSLP signaling pathway map: a platform for analysis of TSLP-mediated signaling
Abstract
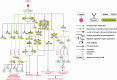
Thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) is a four-helix bundle cytokine that plays a critical role in the regulation of immune responses and in the differentiation of hematopoietic cells. TSLP signals through a heterodimeric receptor complex consisting of an interleukin-7 receptor α chain and a unique TSLP receptor (TSLPR) [also known as cytokine receptor-like factor 2 (CRLF2)]. Cellular targets of TSLP include dendritic cells, B cells, mast cells, regulatory T (Treg) cells and CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. The TSLP/TSLPR axis can activate multiple signaling transduction pathways including the JAK/STAT pathway and the PI-3 kinase pathway. Aberrant TSLP/TSLPR signaling has been associated with a variety of human diseases including asthma, atopic dermatitis, nasal polyposis, inflammatory bowel disease, eosinophilic eosophagitis and, most recently, acute lymphoblastic leukemia. A centralized resource of the TSLP signaling pathway cataloging signaling events is not yet available. In this study, we present a literature-annotated resource of reactions in the TSLP signaling pathway. This pathway map is publicly available through NetPath (http://www.netpath.org/), an open access signal transduction pathway resource developed previously by our group. This map includes 236 molecules and 252 reactions that are involved in TSLP/TSLPR signaling pathway. We expect that the TSLP signaling pathway map will provide a rich resource to study the biology of this important cytokine as well as to identify novel therapeutic targets for diseases associated with dysregulated TSLP/TSLPR signaling. Database URL: http://www.netpath.org/pathways?path_id=NetPath_24.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Expression and Regulation of Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin and Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin Receptor Heterocomplex in the Innate-Adaptive Immunity of Pediatric Asthma.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Apr 18;19(4):1231. doi: 10.3390/ijms19041231. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29670037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thymic stromal lymphopoietin receptor-mediated IL-6 and CC/CXC chemokines expression in human airway smooth muscle cells: role of MAPKs (ERK1/2, p38, and JNK) and STAT3 pathways.J Immunol. 2010 Jun 15;184(12):7134-43. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0902515. Epub 2010 May 14. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20483734
-
Blockage of thymic stromal lymphopoietin signaling improves acute lung injury in mice by regulating pulmonary dendritic cells.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Sep 1;8(9):10698-706. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26617780 Free PMC article.
-
Site-directed mutagenesis reveals a unique requirement for tyrosine residues in IL-7Ralpha and TSLPR cytoplasmic domains in TSLP-dependent cell proliferation.BMC Immunol. 2010 Feb 8;11:5. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-11-5. BMC Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20144186 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-TSLP antibodies: Targeting a master regulator of type 2 immune responses.Allergol Int. 2020 Apr;69(2):197-203. doi: 10.1016/j.alit.2020.01.001. Epub 2020 Jan 21. Allergol Int. 2020. PMID: 31974038 Review.
Cited by
-
In Silico Analysis of Ion Channels and Their Correlation with Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Breast Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Mar 11;14(6):1444. doi: 10.3390/cancers14061444. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35326596 Free PMC article.
-
A network map of Interleukin-10 signaling pathway.J Cell Commun Signal. 2016 Mar;10(1):61-7. doi: 10.1007/s12079-015-0302-x. Epub 2015 Aug 8. J Cell Commun Signal. 2016. PMID: 26253919 Free PMC article.
-
Interstitial Deletions Generating Fusion Genes.Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2021 May-Jun;18(3):167-196. doi: 10.21873/cgp.20251. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2021. PMID: 33893073 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deciphering the Interactions of SARS-CoV-2 Proteins with Human Ion Channels Using Machine-Learning-Based Methods.Pathogens. 2022 Feb 17;11(2):259. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11020259. Pathogens. 2022. PMID: 35215201 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Polycomb RYBP in Maintaining the B-1-to-B-2 B-Cell Lineage Switch in Adult Hematopoiesis.Mol Cell Biol. 2015 Dec 28;36(6):900-12. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00869-15. Mol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26711264 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pandey A, Ozaki K, Baumann H, et al. Cloning of a receptor subunit required for signaling by thymic stromal lymphopoietin. Nat. Immunol. 2000;1:59–64. - PubMed
-
- Friend SL, Hosier S, Nelson A, et al. A thymic stromal cell line supports in vitro development of surface IgM+ B cells and produces a novel growth factor affecting B and T lineage cells. Exp. Hematol. 1994;22:321–328. - PubMed
-
- Levin SD, Koelling RM, Friend SL, et al. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin: a cytokine that promotes the development of IgM+ B cells in vitro and signals via a novel mechanism. J. Immunol. 1999;162:677–683. - PubMed
-
- Liu YJ, Soumelis V, Watanabe N, et al. TSLP: an epithelial cell cytokine that regulates T cell differentiation by conditioning dendritic cell maturation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2007;25:193–219. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

