Benchmarking of methods for genomic taxonomy
- PMID: 24574292
- PMCID: PMC3993634
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.02981-13
Benchmarking of methods for genomic taxonomy
Abstract
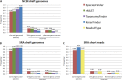
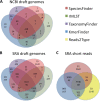
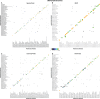
One of the first issues that emerges when a prokaryotic organism of interest is encountered is the question of what it is--that is, which species it is. The 16S rRNA gene formed the basis of the first method for sequence-based taxonomy and has had a tremendous impact on the field of microbiology. Nevertheless, the method has been found to have a number of shortcomings. In the current study, we trained and benchmarked five methods for whole-genome sequence-based prokaryotic species identification on a common data set of complete genomes: (i) SpeciesFinder, which is based on the complete 16S rRNA gene; (ii) Reads2Type that searches for species-specific 50-mers in either the 16S rRNA gene or the gyrB gene (for the Enterobacteraceae family); (iii) the ribosomal multilocus sequence typing (rMLST) method that samples up to 53 ribosomal genes; (iv) TaxonomyFinder, which is based on species-specific functional protein domain profiles; and finally (v) KmerFinder, which examines the number of cooccurring k-mers (substrings of k nucleotides in DNA sequence data). The performances of the methods were subsequently evaluated on three data sets of short sequence reads or draft genomes from public databases. In total, the evaluation sets constituted sequence data from more than 11,000 isolates covering 159 genera and 243 species. Our results indicate that methods that sample only chromosomal, core genes have difficulties in distinguishing closely related species which only recently diverged. The KmerFinder method had the overall highest accuracy and correctly identified from 93% to 97% of the isolates in the evaluations sets.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Reads2Type: a web application for rapid microbial taxonomy identification.BMC Bioinformatics. 2015 Nov 25;16:398. doi: 10.1186/s12859-015-0829-0. BMC Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 26608174 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosomal multilocus sequence typing: universal characterization of bacteria from domain to strain.Microbiology (Reading). 2012 Apr;158(Pt 4):1005-1015. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.055459-0. Epub 2012 Jan 27. Microbiology (Reading). 2012. PMID: 22282518 Free PMC article.
-
A Genus Definition for Bacteria and Archaea Based on a Standard Genome Relatedness Index.mBio. 2020 Jan 14;11(1):e02475-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02475-19. mBio. 2020. PMID: 31937639 Free PMC article.
-
Multilocus sequence analysis (MLSA) in prokaryotic taxonomy.Syst Appl Microbiol. 2015 Jun;38(4):237-45. doi: 10.1016/j.syapm.2015.03.007. Epub 2015 Apr 11. Syst Appl Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25959541 Review.
-
Integrating genomics into the taxonomy and systematics of the Bacteria and Archaea.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2014 Feb;64(Pt 2):316-324. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.054171-0. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24505069 Review.
Cited by
-
Emergence and clonal expansion of Aeromonas hydrophila ST1172 that simultaneously produces MOX-13 and OXA-724.Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2024 Mar 3;13(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s13756-023-01339-4. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2024. PMID: 38433212 Free PMC article.
-
Draft Genome Sequence of Enterobacter cloacae 3D9 (Phylum Proteobacteria).Microbiol Resour Announc. 2018 Oct 25;7(16):e00902-18. doi: 10.1128/MRA.00902-18. eCollection 2018 Oct. Microbiol Resour Announc. 2018. PMID: 30533747 Free PMC article.
-
Draft Genome Sequence of Enterobacter cloacae 3F11 (Phylum Proteobacteria).Microbiol Resour Announc. 2018 Aug 16;7(6):e00846-18. doi: 10.1128/MRA.00846-18. eCollection 2018 Aug. Microbiol Resour Announc. 2018. PMID: 30533901 Free PMC article.
-
The Distribution of Campylobacter jejuni Virulence Genes in Genomes Worldwide Derived from the NCBI Pathogen Detection Database.Genes (Basel). 2021 Sep 28;12(10):1538. doi: 10.3390/genes12101538. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34680933 Free PMC article.
-
Genome Sequences of Clinical Isolates of NDM-1-Producing Klebsiella quasipneumoniae subsp. similipneumoniae and KPC-2-Producing Klebsiella quasipneumoniae subsp. quasipneumoniae from Brazil.Microbiol Resour Announc. 2020 Mar 5;9(10):e00089-20. doi: 10.1128/MRA.00089-20. Microbiol Resour Announc. 2020. PMID: 32139569 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fox GE, Peckman KJ, Woese CE. 1977. Comparative cataloging of 16S ribosomal ribonucleic acid: molecular approach to procaryotic systematics. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Bacteriol. 27:44–57. 10.1099/00207713-27-1-44 - DOI
-
- Ludwig W, Strunk O, Westram R, Richter L, Meier H, Yadhukumar Buchner A, Lai T, Steppi S, Jobb G, Forster W, Brettske I, Gerber S, Ginhart AW, Gross O, Grumann S, Hermann S, Jost R, Konig A, Liss T, Lussmann R, May M, Nonhoff B, Reichel B, Strehlow R, Stamatakis A, Stuckmann N, Vilbig A, Lenke M, Ludwig T, Bode A, Schleifer KH. 2004. ARB: a software environment for sequence data. Nucleic Acids Res. 32:1363–1371. 10.1093/nar/gkh293 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

