Association of exhaled carbon monoxide with subclinical cardiovascular disease and their conjoint impact on the incidence of cardiovascular outcomes
- PMID: 24574370
- PMCID: PMC4271053
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehu052
Association of exhaled carbon monoxide with subclinical cardiovascular disease and their conjoint impact on the incidence of cardiovascular outcomes
Abstract
Aims: Whereas endogenous carbon monoxide (CO) is cytoprotective at physiologic levels, excess CO concentrations are associated with cardiometabolic risk and may represent an important marker of progression from subclinical to clinical cardiovascular disease (CVD).
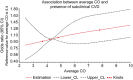
Methods and results: In 1926 participants of the Framingham Offspring Study (aged 57 ± 10 years, 46% women), we investigated the relationship of exhaled CO, a surrogate of blood CO concentration, with both prevalent subclinical CVD and incident clinical CVD events. Presence of subclinical CVD was determined using a comprehensive panel of diagnostic tests used to assess cardiac and vascular structure and function. Individuals with the highest (>5 p.p.m.) compared with lowest (≤4 p.p.m.) CO exposure were more likely to have subclinical CVD [odds ratios (OR): 1.67, 95% CI: 1.32-2.12; P < 0.001]. During the follow-up period (mean 5 ± 3 years), 193 individuals developed overt CVD. Individuals with both high CO levels and any baseline subclinical CVD developed overt CVD at an almost four-fold higher rate compared with those with low CO levels and no subclinical disease (22.1 vs. 6.3%). Notably, elevated CO was associated with incident CVD in the presence [hazards ration (HR): 1.83, 95% CI: 1.08-3.11; P = 0.026] but not in the absence (HR: 0.80, 95% CI: 0.42-1.53; P = 0.51) of subclinical CVD (Pinteraction = 0.019). Similarly, subclinical CVD was associated with incident CVD in the presence of high but not low CO exposure.
Conclusion: Our findings in a community-based sample suggest that elevated CO is a marker of greater subclinical CVD burden and, furthermore, a potential key component in the progression from subclinical to clinical CVD.
Keywords: Carbon monoxide; Cardiovascular outcomes; Subclinical vascular disease.
Published on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology. All rights reserved. © The Author 2014. For permissions please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures


References
-
- Durante W. Carbon monoxide and bile pigments: surprising mediators of vascular function. Vasc Med. 2002;7:195–202. - PubMed
-
- Wang X, Wang Y, Kim HP, Nakahira K, Ryter SW, Choi AM. Carbon monoxide protects against hyperoxia-induced endothelial cell apoptosis by inhibiting reactive oxygen species formation. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:1718–1726. - PubMed
-
- Ndisang JF, Tabien HE, Wang R. Carbon monoxide and hypertension. J Hypertens. 2004;22:1057–1074. - PubMed
-
- Chan KH, Ng MK, Stocker R. Haem oxygenase-1 and cardiovascular disease: mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Clin Sci (Lond) 2011;120:493–504. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

