Genome scale patterns of recombination between coinfecting vaccinia viruses
- PMID: 24574414
- PMCID: PMC4019122
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00022-14
Genome scale patterns of recombination between coinfecting vaccinia viruses
Abstract
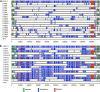
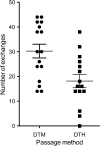
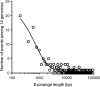
Recombination plays a critical role in virus evolution. It helps avoid genetic decline and creates novel phenotypes. This promotes survival, and genome sequencing suggests that recombination has facilitated the evolution of human pathogens, including orthopoxviruses such as variola virus. Recombination can also be used to map genes, but although recombinant poxviruses are easily produced in culture, classical attempts to map the vaccinia virus (VACV) genome this way met with little success. We have sequenced recombinants formed when VACV strains TianTan and Dryvax are crossed under different conditions. These were a single round of growth in coinfected cells, five rounds of sequential passage, or recombinants obtained using leporipoxvirus-mediated DNA reactivation. Our studies showed that recombinants contain a patchwork of DNA, with the number of exchanges increasing with passage. Further passage also selected for TianTan DNA and correlated with increased plaque size. The recombinants produced through a single round of coinfection contain a disproportionate number of short conversion tracks (<1 kbp) and exhibited 1 exchange per 12 kbp, close to the ∼1 per 8 kbp in the literature. One by-product of this study was that rare mutations were also detected; VACV replication produces ∼1×10(-8) mutation per nucleotide copied per cycle of replication and ∼1 large (21 kbp) deletion per 70 rounds of passage. Viruses produced using DNA reactivation appeared no different from recombinants produced using ordinary methods. An attractive feature of this approach is that when it is combined with selection for a particular phenotype, it provides a way of mapping and dissecting more complex virus traits.
Importance: When two closely related viruses coinfect the same cell, they can swap genetic information through a process called recombination. Recombination produces new viruses bearing different combinations of genes, and it plays an important role in virus evolution. Poxviruses are a family of viruses that includes variola (or smallpox) virus, and although poxviruses are known to recombine, no one has previously mapped the patterns of DNAs exchanged between viruses. We coinfected cells with two different vaccinia poxviruses, isolated the progeny, and sequenced them. We show that poxvirus recombination is a very accurate process that assembles viruses containing DNA copied from both parents. In a single round of infection, DNA is swapped back and forth ∼18 times per genome to make recombinant viruses that are a mosaic of the two parental DNAs. This mixes many different genes in complex combinations and illustrates how recombination can produce viruses with greatly altered disease potential.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Evolution of and evolutionary relationships between extant vaccinia virus strains.J Virol. 2015 Feb;89(3):1809-24. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02797-14. Epub 2014 Nov 19. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25410873 Free PMC article.
-
Inactivation of Genes by Frameshift Mutations Provides Rapid Adaptation of an Attenuated Vaccinia Virus.J Virol. 2020 Aug 31;94(18):e01053-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01053-20. Print 2020 Aug 31. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32669330 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccinia Virus Gene Acquisition through Nonhomologous Recombination.J Virol. 2021 Jun 24;95(14):e0031821. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00318-21. Epub 2021 Jun 24. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33910949 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of recombinant vaccinia viruses using leporipoxvirus-catalyzed recombination and reactivation of orthopoxvirus DNA.Methods Mol Biol. 2004;269:51-64. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-789-0:051. Methods Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 15114007 Review.
-
Construction of cDNA libraries in vaccinia virus.Methods Mol Biol. 2004;269:65-76. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-789-0:065. Methods Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 15114008 Review.
Cited by
-
Genomic Characterization of the Historical Smallpox Vaccine Strain Wyeth Isolated from a 1971 Seed Vial.Viruses. 2022 Dec 28;15(1):83. doi: 10.3390/v15010083. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36680123 Free PMC article.
-
A T cell-targeted multi-antigen vaccine generates robust cellular and humoral immunity against SARS-CoV-2 infection.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2023 Sep 16;31:101110. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2023.101110. eCollection 2023 Dec 14. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2023. PMID: 37822719 Free PMC article.
-
Monkeypox Outbreak 2022, from a Rare Disease to Global Health Emergence: Implications for Travellers.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1451:355-368. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-57165-7_23. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 38801590 Review.
-
Monkeypox: disease epidemiology, host immunity and clinical interventions.Nat Rev Immunol. 2022 Oct;22(10):597-613. doi: 10.1038/s41577-022-00775-4. Epub 2022 Sep 5. Nat Rev Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36064780 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Deep-Sequencing Workflow for the Fast and Efficient Generation of High-Quality African Swine Fever Virus Whole-Genome Sequences.Viruses. 2019 Sep 11;11(9):846. doi: 10.3390/v11090846. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 31514438 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fenner F, Comben BM. 1958. Genetic studies with mammalian poxviruses. I. Demonstration of recombination between two strains of vaccinia virus. Virology 5:530–548 - PubMed
-
- Woodroofe GM, Fenner F. 1960. Genetic studies with mammalian poxviruses. IV. Hybridization between several different poxviruses. Virology 12:272–282 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

