Effects of pentoxifylline on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 24574727
- PMCID: PMC3923033
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i2.569
Effects of pentoxifylline on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the effects of pentoxifylline therapy in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Methods: We searched PubMed, Medline, Google Scholar, Embase, Web of Science, the Cochrane Library and the Chinese Biomedicine Database for all relevant controlled trials of pentoxifylline in patients with NAFLD from 1997 to July 2013. Five studies (3 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials and 2 prospective cohort studies with concurrent controls) were included in this meta-analysis. Statistical analysis was performed using RevMan 5.0 software.
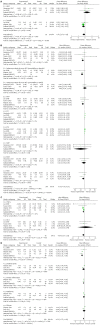
Results: Five randomized trials of 147 patients with NAFLD/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) were included. The results showed that compared to placebo, pentoxifylline therapy resulted in a significant decrease in body weight (P = 0.04), alanine aminotransferase (P < 0.00001), aspartate transaminase (P = 0.0006), glucose (P = 0.0008) and tumor necrosis factor-α (P = 0.007), but did not significantly affect body mass index (P = 0.28), total cholesterol (P = 0.80), triglyceride (P = 0.98), alkaline phosphatase (P = 0.29), γ-glutamyl transferase (P = 0.39) and interleukin-6 (P = 0.38). With regard to histological changes, pentoxifylline only reduced the NAFLD activity score (P < 0.00001) and improved lobular inflammation (P < 0.0001). Improvements in steatosis grade (P = 0.11), ballooning (P = 0.10) and fibrosis (P = 0.50) were not obvious.
Conclusion: Pentoxifylline therapy results in weight loss, improved liver function and histological changes in patients with NAFLD/NASH. Therefore, pentoxifylline may be a new treatment option for NAFLD.
Keywords: Meta-analysis; Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis; Pentoxifylline.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pentoxifylline for the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a meta-analysis of randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled studies.Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014 Jun;26(6):646-53. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000000068. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 24743504
-
Effects of probiotics on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a meta-analysis.World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Oct 28;19(40):6911-8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i40.6911. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 24187469 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vitamin E has a beneficial effect on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Nutrition. 2015 Jul-Aug;31(7-8):923-30. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2014.11.018. Epub 2014 Dec 24. Nutrition. 2015. PMID: 26059365
-
Pentoxifylline improves nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a randomized placebo-controlled trial.Hepatology. 2011 Nov;54(5):1610-9. doi: 10.1002/hep.24544. Epub 2011 Aug 24. Hepatology. 2011. PMID: 21748765 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Does turmeric/curcumin supplementation improve serum alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase levels in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease? A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Phytother Res. 2019 Mar;33(3):561-570. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6270. Epub 2019 Jan 17. Phytother Res. 2019. PMID: 30653773
Cited by
-
The Role of Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Curr Obes Rep. 2023 Sep;12(3):191-206. doi: 10.1007/s13679-023-00519-y. Epub 2023 Jul 5. Curr Obes Rep. 2023. PMID: 37407724 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease as risk factor for drug-induced hepatotoxicity.J Clin Transl Res. 2017 Feb;3(Suppl 1):212-232. doi: 10.18053/jctres.03.2017S1.006. Epub 2017 Feb 12. J Clin Transl Res. 2017. PMID: 28691103 Free PMC article.
-
Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Endpoints in Clinical Trials.Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2016 Dec;12(12):756-763. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2016. PMID: 28035202 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Targets and Approaches to Manage Inflammation of NAFLD.Biomedicines. 2025 Feb 6;13(2):393. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13020393. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40002806 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innovative Therapeutic Approaches in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: When Knowing Your Patient Is Key.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 27;24(13):10718. doi: 10.3390/ijms241310718. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37445895 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ong JP, Younossi ZM. Epidemiology and natural history of NAFLD and NASH. Clin Liver Dis. 2007;11:1–16, vii. - PubMed
-
- Adams LA, Angulo P. Recent concepts in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Diabet Med. 2005;22:1129–1133. - PubMed
-
- Marchesini G, Brizi M, Bianchi G, Tomassetti S, Zoli M, Melchionda N. Metformin in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Lancet. 2001;358:893–894. - PubMed
-
- Uygun A, Kadayifci A, Isik AT, Ozgurtas T, Deveci S, Tuzun A, Yesilova Z, Gulsen M, Dagalp K. Metformin in the treatment of patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2004;19:537–544. - PubMed
-
- Promrat K, Lutchman G, Uwaifo GI, Freedman RJ, Soza A, Heller T, Doo E, Ghany M, Premkumar A, Park Y, et al. A pilot study of pioglitazone treatment for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 2004;39:188–196. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

