Antinociceptive effects of novel melatonin receptor agonists in mouse models of abdominal pain
- PMID: 24574803
- PMCID: PMC3921511
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i5.1298
Antinociceptive effects of novel melatonin receptor agonists in mouse models of abdominal pain
Abstract
Aim: To characterize the antinociceptive action of the novel melatonin receptor (MT) agonists, Neu-P11 and Neu-P12 in animal models of visceral pain.
Methods: Visceral pain was induced by intracolonic (ic) application of mustard oil or capsaicin solution or by intraperitoneal (ip) administration of acetic acid. Neu-P11, Neu-P12, or melatonin were given ip or orally and their effects on pain-induced behavioral responses were evaluated. To identify the receptors involved, the non-selective MT1/MT2 receptor antagonist luzindole, the MT2 receptor antagonist 4-P-PDOT, or the μ-opioid receptor antagonist naloxone were injected ip or intracerebroventricularly (icv) prior to the induction of pain.
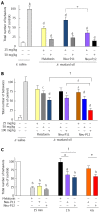
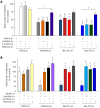
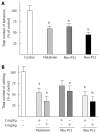
Results: Orally and ip administered melatonin, Neu-P11, and Neu-P12 reduced pain responses in a dose-dependent manner. Neu-P12 was more effective and displayed longer duration of action compared to melatonin. The antinociceptive effects of Neu-P11 or Neu-P12 were antagonized by ip or icv. administered naloxone. Intracerebroventricularly, but not ip administration of luzindole or 4-P-PDOT blocked the antinociceptive actions of Neu-P11 or Neu-P12.
Conclusion: Neu-P12 produced the most potent and long-lasting antinociceptive effect. Further development of Neu-P12 for future treatment of abdominal pain seems promising.
Keywords: Gastrointestinal tract; Melatonin; Neu-P11; Neu-P12; Opioid; Visceral pain.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exogenous melatonin abolishes mechanical allodynia but not thermal hyperalgesia in neuropathic pain. The role of the opioid system and benzodiazepine-gabaergic mechanism.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012 Dec;63(6):641-7. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 23388480
-
Piromelatine exerts antinociceptive effect via melatonin, opioid, and 5HT1A receptors and hypnotic effect via melatonin receptors in a mouse model of neuropathic pain.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014 Oct;231(20):3973-85. doi: 10.1007/s00213-014-3530-5. Epub 2014 Apr 4. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014. PMID: 24700387
-
Melatonin, but not melatonin receptor agonists Neu-P11 and Neu-P67, attenuates TNBS-induced colitis in mice.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2016 May;389(5):511-9. doi: 10.1007/s00210-016-1214-x. Epub 2016 Feb 22. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26899972 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin and its agonists in pain modulation and its clinical application.Arch Ital Biol. 2012 Dec;150(4):274-89. doi: 10.4449/aib.v150i4.1391. Arch Ital Biol. 2012. PMID: 23479460 Review.
-
Biological action of melatonin on target receptors in breast cancer.Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 2024 Apr 22;70(3):e20231260. doi: 10.1590/1806-9282.20231260. eCollection 2024. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 2024. PMID: 38656007 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Efficacy and Safety of Agomelatine in Depressed Patients with Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 25;25(23):12631. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312631. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684343 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic applications of melatonin in disorders related to the gastrointestinal tract and control of appetite.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Aug;397(8):5335-5362. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-02972-5. Epub 2024 Feb 15. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38358468 Review.
-
Salvinorin A analogues PR-37 and PR-38 attenuate compound 48/80-induced itch responses in mice.Br J Pharmacol. 2015 Sep;172(17):4331-41. doi: 10.1111/bph.13212. Epub 2015 Jul 14. Br J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26040667 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Melatonin in the Regulation of Pain.J Pain Res. 2020 Feb 7;13:331-343. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S228577. eCollection 2020. J Pain Res. 2020. PMID: 32104055 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Influence of Sleep Disturbance on Chronic Pain.Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2022 Oct;26(10):795-804. doi: 10.1007/s11916-022-01074-2. Epub 2022 Oct 3. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2022. PMID: 36190680 Review.
References
-
- Maestroni GJ. The immunotherapeutic potential of melatonin. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2001;10:467–476. - PubMed
-
- Maldonado MD, Mora-Santos M, Naji L, Carrascosa-Salmoral MP, Naranjo MC, Calvo JR. Evidence of melatonin synthesis and release by mast cells. Possible modulatory role on inflammation. Pharmacol Res. 2010;62:282–287. - PubMed
-
- Conti A, Conconi S, Hertens E, Skwarlo-Sonta K, Markowska M, Maestroni JM. Evidence for melatonin synthesis in mouse and human bone marrow cells. J Pineal Res. 2000;28:193–202. - PubMed
-
- Messner M, Huether G, Lorf T, Ramadori G, Schwörer H. Presence of melatonin in the human hepatobiliary-gastrointestinal tract. Life Sci. 2001;69:543–551. - PubMed
-
- Brzezinski A. Melatonin in humans. N Engl J Med. 1997;336:186–195. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

