Hepatoduodenal fistula formation following transcatheter arterial chemoembolization and radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: treatment with endoscopic Histoacryl injection
- PMID: 24574839
- PMCID: PMC3932379
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2014.29.1.101
Hepatoduodenal fistula formation following transcatheter arterial chemoembolization and radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: treatment with endoscopic Histoacryl injection
Abstract
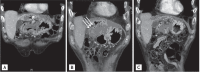
A 71-year-old male patient was readmitted to our hospital 1 month after discharge because of relapse of abdominal pain. He had been diagnosed with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) 1 year prior and had undergone repeated transcatheter arterial chemoembolization and radiotherapy. During the last hospitalization, he was diagnosed with a liver abscess complicated by previous treatments for HCC and was treated with intravenous antibiotics and abscess aspiration. Follow-up abdominal computed tomography revealed a liver abscess with a duodenal fistula, which was successfully treated with endoscopic Histoacryl injection into the fistula. Liver abscesses with duodenal fistulas rarely occur, but they are intractable and possibly fatal in patients with HCC. In the literature, they have frequently been managed only with abscess treatment without fistula management. We herein report the first case of a patient with a liver abscess complicated by a fistula between the duodenum and the abscess, which was treated with endoscopic Histoacryl injection.
Keywords: Abscess; Carcinoma, hepatocellular; Endoscopy; Fistula.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article is reported.
Figures


References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Lee JS. Advances in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Korean J Med. 2009;77:290–297.
-
- Wang CY, Leung SW, Wang JH, Yu PC, Wang CC. Delayed spontaneous hepatogastric f istula formation following transcatheter arterial embolisation and radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Radiol. 2009;82:e105–e107. - PubMed
-
- Meng MB, Cui YL, Lu Y, et al. Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in combination with radiotherapy for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Radiother Oncol. 2009;92:184–194. - PubMed
-
- Marelli L, Stigliano R, Triantos C, et al. Transarterial therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: which technique is more effective? A systematic review of cohort and randomized studies. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2007;30:6–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
