Enhanced synaptic transmission at the squid giant synapse by artificial seawater based on physically modified saline
- PMID: 24575037
- PMCID: PMC3921564
- DOI: 10.3389/fnsyn.2014.00002
Enhanced synaptic transmission at the squid giant synapse by artificial seawater based on physically modified saline
Abstract
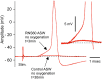
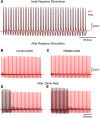
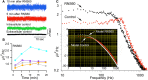
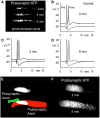
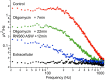
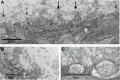
Superfusion of the squid giant synapse with artificial seawater (ASW) based on isotonic saline containing oxygen nanobubbles (RNS60 ASW) generates an enhancement of synaptic transmission. This was determined by examining the postsynaptic response to single and repetitive presynaptic spike activation, spontaneous transmitter release, and presynaptic voltage clamp studies. In the presence of RNS60 ASW single presynaptic stimulation elicited larger postsynaptic potentials (PSP) and more robust recovery from high frequency stimulation than in control ASW. Analysis of postsynaptic noise revealed an increase in spontaneous transmitter release with modified noise kinetics in RNS60 ASW. Presynaptic voltage clamp demonstrated an increased EPSP, without an increase in presynaptic ICa(++) amplitude during RNS60 ASW superfusion. Synaptic release enhancement reached stable maxima within 5-10 min of RNS60 ASW superfusion and was maintained for the entire recording time, up to 1 h. Electronmicroscopic morphometry indicated a decrease in synaptic vesicle density and the number at active zones with an increase in the number of clathrin-coated vesicles (CCV) and large endosome-like vesicles near junctional sites. Block of mitochondrial ATP synthesis by presynaptic injection of oligomycin reduced spontaneous release and prevented the synaptic noise increase seen in RNS60 ASW. After ATP block the number of vesicles at the active zone and CCV was reduced, with an increase in large vesicles. The possibility that RNS60 ASW acts by increasing mitochondrial ATP synthesis was tested by direct determination of ATP levels in both presynaptic and postsynaptic structures. This was implemented using luciferin/luciferase photon emission, which demonstrated a marked increase in ATP synthesis following RNS60 administration. It is concluded that RNS60 positively modulates synaptic transmission by up-regulating ATP synthesis, thus leading to synaptic transmission enhancement.
Keywords: calcium current; neurotransmitter release; physically modified water; squid giant synapse; synaptic transmission optimization.
Figures



Similar articles
-
RNS60, a charge-stabilized nanostructure saline alters Xenopus Laevis oocyte biophysical membrane properties by enhancing mitochondrial ATP production.Physiol Rep. 2015 Mar;3(3):e12261. doi: 10.14814/phy2.12261. Physiol Rep. 2015. PMID: 25742953 Free PMC article.
-
The inositol high-polyphosphate series blocks synaptic transmission by preventing vesicular fusion: a squid giant synapse study.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 20;91(26):12990-3. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.26.12990. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994. PMID: 7809161 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation by synapsin I and Ca(2+)-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II of the transmitter release in squid giant synapse.J Physiol. 1991 May;436:257-82. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018549. J Physiol. 1991. PMID: 1676419 Free PMC article.
-
Presynaptic Black Box Opened by Pioneers at Biophysics Department in University College London.Neuroscience. 2020 Jul 15;439:10-21. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.04.029. Epub 2019 May 18. Neuroscience. 2020. PMID: 31108128 Review.
-
Effects of neurotoxicants on synaptic transmission: lessons learned from electrophysiological studies.Neurotoxicol Teratol. 1988 Sep-Oct;10(5):393-416. doi: 10.1016/0892-0362(88)90001-3. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 1988. PMID: 2854607 Review.
Cited by
-
Potential Benefit of the Charge-Stabilized Nanostructure Saline RNS60 for Myelin Maintenance and Repair.Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 25;6:30020. doi: 10.1038/srep30020. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27451946 Free PMC article.
-
Immunological and Metabolic Causes of Infertility in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome.Biomedicines. 2023 May 28;11(6):1567. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11061567. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37371662 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of various types of extracellular DNA on V. hyugaensis biofilm formation.mSphere. 2023 Aug 24;8(4):e0003523. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00035-23. Epub 2023 Jun 30. mSphere. 2023. PMID: 37387577 Free PMC article.
-
RNS60, a charge-stabilized nanostructure saline alters Xenopus Laevis oocyte biophysical membrane properties by enhancing mitochondrial ATP production.Physiol Rep. 2015 Mar;3(3):e12261. doi: 10.14814/phy2.12261. Physiol Rep. 2015. PMID: 25742953 Free PMC article.
-
Oligodendrocyte Dysfunction in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Perspectives.Cells. 2021 Mar 5;10(3):565. doi: 10.3390/cells10030565. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33807572 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

