A Comparison between Hippurate Hydrolysis and Multiplex PCR for Differentiating Campylobacter coli and Campylobacter jejuni
- PMID: 24575212
- PMCID: PMC3819090
A Comparison between Hippurate Hydrolysis and Multiplex PCR for Differentiating Campylobacter coli and Campylobacter jejuni
Abstract
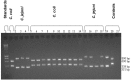
Species identification is important for epidemiological, clinical and treatment purposes. The aim of this study was to find out whether hippurate hydrolysis is a reliable test for differentiating between Campylobacter coli and Campylobacter jejuni. To achieve this, hippurate hydrolysis test was compared with multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction (mPCR) for their ability to speciate C. coli and C. jejuni. Eighteen Campylobacter strains from poultry samples were used for this study. The results from 17 of the 18 strains were in agreement with both methods. Thus, the hippurate hydrolysis test can be used for distinguishing C. jejuni from C. coli although occasionally some strains of C. jejuni may be mis-identified as C. coli.
Pengenalpastian spesies penting untuk tujuan epidemiologikal, klinikal dan perubatan. Tujuan kajian ini adalah untuk mengetahui sama ada ujian hidrolisis hippurate berkesan untuk membezakan antara Campylobacter coli dan Campylobacter jejuni. Untuk mencapai ini, ujian hidrolis hippurate dibandingkan dengan multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction (mPCR) untuk mengkaji kebolehan membezakan spesies C. coli dan C. jejuni. Lapan belas strain Campylobacter daripada sampel haiwan ternakan digunakan. Keputusan 17 daripada 18 strain menunjukkan keberkesanan menggunakan kedua-dua jenis ujian. Maka ujian hidrolisis hippurate berkesan untuk membezakan C. jejuni daripada C. coli, walaupun kadang-kadang terdapat strain C. jejuni yang diidentifikasi secara salah sebagai C. coli.
Keywords: C. coli; C. jejuni; Hippurate Hydrolysis; mPCR.
Figures

References
-
- Adzitey F, Nurul H. Campylobacter in poultry: Incidences and possible control measures. Research Journal of Microbiology. 2011;6(2):182–192.
-
- Bang DD, Wedderkopp A, Pedersen K, Madsen M. Rapid PCR using nested primers of the 16S rRNA and hippuricase (hip O) genes to detect Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli in environmental samples. Molecular and Cellular Probes. 2002;16(5):359–369. - PubMed
-
- Burnett TA, Hornitzky MA, Kuhnert P, Djordjevic SP. Speciating Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli isolates from poultry and humans using six PCR-based assays. FEMS Microbiology Letters. 2002;216(2):201–209. - PubMed
-
- Corry JEL, Atabay HI, Forsythe SJ, Mansfield LP. Culture media for the isolation of campylobacters, helicobacters and arcobacters. In: Corry JEL, Curtis GDW, Baird RM, editors. Handbook of culture media for food microbiology. 2nd ed. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science; 2003. pp. 271–316.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
