Autocrine motility factor modulates EGF-mediated invasion signaling
- PMID: 24576828
- PMCID: PMC4091754
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-2937
Autocrine motility factor modulates EGF-mediated invasion signaling
Abstract
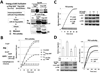
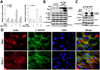
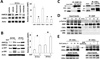
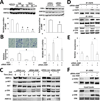
Autocrine motility factor (AMF) enhances invasion by breast cancer cells, but how its secretion and effector signaling are controlled in the tumor microenvironment is not fully understood. In this study, we investigated these issues with a chimeric AMF that is secreted at high levels through a canonical endoplasmic reticulum (ER)/Golgi pathway. Using this tool, we found that AMF enhances tumor cell motility by activating AKT/ERK, altering actin organization, and stimulating β-catenin/TCF and activating protein 1 transcription. EGF enhanced secretion of AMF through its casein kinase II-mediated phosphorylation. RNA interference-mediated attenuation of AMF expression inhibited EGF-induced invasion by suppressing extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling. Conversely, exogenous AMF overcame the inhibitory effect of EGF receptor inhibitor gefitinib on invasive motility by activating HER2 signaling. Taken together, our findings show how AMF modulates EGF-induced invasion while affecting acquired resistance to cytotoxic drugs in the tumor microenvironment.
©2014 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no potential conflicts to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Watanabe H, Takehana K, Date M, Shinozaki T, Raz A. Tumor cell autocrine motility factor is the neuroleukin/phosphohexose isomerase polypeptide. Cancer Res. 1996;56:2960–2963. - PubMed
-
- Gurney ME. Neuroleukin: basic biology and functional interaction with human immunodeficiency virus. Immunol Rev. 1987;100:203–223. - PubMed
-
- Xu W, Seiter K, Feldman E, Ahmed T, Chiao JW. The differentiation and maturation mediator for human myeloid leukemia cells shares homology with neuroleukin or phosphoglucose isomerase. Blood. 1996;87:4502–4506. - PubMed
-
- Fairbank M, St-Pierre P, Nabi IR. The complex biology of autocrine motility factor/phosphoglucose isomerase (AMF/PGI) and its receptor, the gp78/AMFR E3 ubiquitin ligase. Mol Biosyst. 2009;5:793–801. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

