Optimized lentiviral vectors for HIV gene therapy: multiplexed expression of small RNAs and inclusion of MGMT(P140K) drug resistance gene
- PMID: 24576853
- PMCID: PMC4015224
- DOI: 10.1038/mt.2014.32
Optimized lentiviral vectors for HIV gene therapy: multiplexed expression of small RNAs and inclusion of MGMT(P140K) drug resistance gene
Abstract
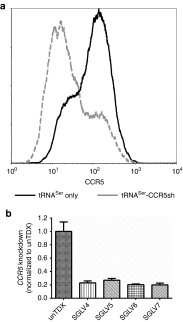
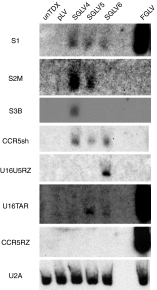
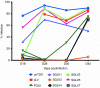
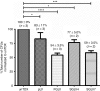
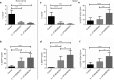
Gene therapy with hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells is a promising approach to engineering immunity to human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) that may lead to a functional cure for acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). In support of this approach, we created lentiviral vectors with an engineered polycistronic platform derived from the endogenous MCM7 gene to express a diverse set of small antiviral RNAs and a drug resistance MGMT(P140K) marker. Multiple strategies for simultaneous expression of up to five RNA transgenes were tested. The placement and orientation of each transgene and its promoter were important determinants for optimal gene expression. Antiviral RNA expression from the MCM7 platform with a U1 promoter was sufficient to provide protection from R5-tropic HIV in macrophages and resulted in reduced hematopoietic toxicity compared with constructs expressing RNA from independent RNA polymerase III promoters. The addition of an HIV entry inhibitor and nucleolar TAR RNA decoy did not enhance antiviral potency over constructs that targeted only viral RNA transcripts. We also demonstrated selective enrichment of gene-modified cells in vivo using a humanized mouse model. The use of these less toxic, potent anti-HIV vectors expressing a drug selection marker is likely to enhance the in vivo efficacy of our stem cell gene therapy approach in treating HIV/AIDS.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization (October 2013). HIV/AIDS Fac Sheet N*360.
-
- Calza L. Renal toxicity associated with antiretroviral therapy. HIV Clin Trials. 2012;13:189–211. - PubMed
-
- Jones M, Núñez M. Liver toxicity of antiretroviral drugs. Semin Liver Dis. 2012;32:167–176. - PubMed
-
- Lipshultz SE, Mas CM, Henkel JM, Franco VI, Fisher SD, Miller TL. HAART to heart: highly active antiretroviral therapy and the risk of cardiovascular disease in HIV-infected or exposed children and adults. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2012;10:661–674. - PubMed
-
- Domingo P, Estrada V, López-Aldeguer J, Villaroya F, Martínez E. Fat redistribution syndromes associated with HIV-1 infection and combination antiretroviral therapy. AIDS Rev. 2012;14:112–123. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

