Reduced hepatic eNOS phosphorylation is associated with NAFLD and type 2 diabetes progression and is prevented by daily exercise in hyperphagic OLETF rats
- PMID: 24577062
- PMCID: PMC4097825
- DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01275.2013
Reduced hepatic eNOS phosphorylation is associated with NAFLD and type 2 diabetes progression and is prevented by daily exercise in hyperphagic OLETF rats
Abstract
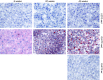
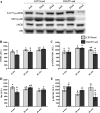
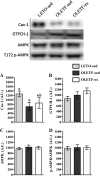
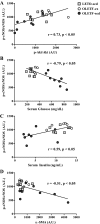
We tested the hypothesis that nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is associated with reduced hepatic endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) activation status via S1177 phosphorylation (p-eNOS) and is prevented by daily voluntary wheel running (VWR). Hyperphagic Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty (OLETF) rats, an established model of obesity, type 2 diabetes (T2D) and NAFLD, and normophagic controls [Long-Evans Tokushima Otsuka (LETO)] were studied at 8, 20, and 40 wk of age. Basal hepatic eNOS phosphorylation (p-eNOS/eNOS) was similar between LETO and OLETFs with early hepatic steatosis (8 wk of age) and advanced steatosis, hyperinsulinemia, and hyperglycemia (20 wk of age). In contrast, hepatic p-eNOS/eNOS was significantly lower (P < 0.05) in OLETF rats with T2D advancement and the transition to more advanced NAFLD with inflammation and fibrosis [increased tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), CD68, and CD163 mRNA expression; 40 wk of age]. Reduced hepatic eNOS activation status in 40-wk OLETF rats was significantly correlated with reduced p-Akt/Akt (r = 0.73, P < 0.05), reduced serum insulin (r = 0.59, P < 0.05), and elevated serum glucose (r = -0.78, P < 0.05), suggesting a link between impaired glycemic control and altered hepatic nitric oxide metabolism. VWR by OLETF rats, in conjunction with NAFLD and T2D prevention, normalized p-eNOS/eNOS and p-Akt/Akt to LETO levels. Basal activation of hepatic eNOS and Akt are maintained until advanced NAFLD and T2D development in obese OLETF rats. The prevention of this reduction by VWR may result from maintained insulin sensitivity and glycemic control.
Keywords: Akt; OLETF; eNOS; exercise; hepatic; type 2 diabetes.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Daily exercise vs. caloric restriction for prevention of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the OLETF rat model.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011 May;300(5):G874-83. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00510.2010. Epub 2011 Feb 24. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21350190 Free PMC article.
-
Physical activity maintains aortic endothelium-dependent relaxation in the obese type 2 diabetic OLETF rat.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010 Jun;298(6):H1889-901. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.01252.2009. Epub 2010 Mar 19. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20304812 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic NOS inhibition accelerates NAFLD progression in an obese rat model.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015 Mar 15;308(6):G540-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00247.2014. Epub 2015 Jan 8. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25573175 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperphagia and obesity of OLETF rats lacking CCK1 receptors: developmental aspects.Dev Psychobiol. 2006 Jul;48(5):360-7. doi: 10.1002/dev.20149. Dev Psychobiol. 2006. PMID: 16770763 Review.
-
Unraveling the obesity of OLETF rats.Physiol Behav. 2008 Apr 22;94(1):71-8. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2007.11.035. Epub 2007 Nov 29. Physiol Behav. 2008. PMID: 18190934 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mitochondrial metabolic dysfunction and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: new insights from pathogenic mechanisms to clinically targeted therapy.J Transl Med. 2023 Jul 28;21(1):510. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04367-1. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37507803 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathophysiological Features of Rat Models of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease/Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis.In Vivo. 2024 May-Jun;38(3):990-999. doi: 10.21873/invivo.13532. In Vivo. 2024. PMID: 38688597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
eNOS deletion impairs mitochondrial quality control and exacerbates Western diet-induced NASH.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2019 Oct 1;317(4):E605-E616. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00096.2019. Epub 2019 Jul 30. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2019. PMID: 31361543 Free PMC article.
-
The Emerging Role of Hepatocellular eNOS in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Development.Front Physiol. 2020 Jul 3;11:767. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00767. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32719616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alpinetin: A Review of Its Pharmacology and Pharmacokinetics.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Feb 4;13:814370. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.814370. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35185569 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Browning JD, Szczepaniak LS, Dobbins R, Nuremberg P, Horton JD, Cohen JC, Grundy SM, Hobbs HH. Prevalence of hepatic steatosis in an urban population in the United States: impact of ethnicity. Hepatology 40: 1387–1395, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Chen ZP, Mitchelhill KI, Michell BJ, Stapleton D, Rodriguez-Crespo I, Witters LA, Power DA, Ortiz de Montellano PR, Kemp BE. AMP-activated protein kinase phosphorylation of endothelial NO synthase. FEBS Lett 443: 285–289, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Chen Z, Bakhshi FR, Shajahan AN, Sharma T, Mao M, Trane A, Bernatchez P, van Nieuw Amerongen GP, Bonini MG, Skidgel RA, Malik AB, Minshall RD. Nitric oxide-dependent Src activation and resultant caveolin-1 phosphorylation promote eNOS/caveolin-1 binding and eNOS inhibition. Mol Biol Cell 23: 1388–1398, 2012 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

