PTEN regulates AMPA receptor-mediated cell viability in iPS-derived motor neurons
- PMID: 24577094
- PMCID: PMC3944269
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2014.55
PTEN regulates AMPA receptor-mediated cell viability in iPS-derived motor neurons
Abstract
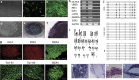
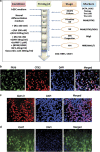
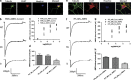
Excitatory transmission in the brain is commonly mediated by the α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid (AMPA) receptors. In amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), AMPA receptors allow cytotoxic levels of calcium into neurons, contributing to motor neuron injury. We have previously shown that oculomotor neurons resistant to the disease process in ALS show reduced AMPA-mediated inward calcium currents compared with vulnerable spinal motor neurons. We have also shown that PTEN (phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10) knockdown via siRNA promotes motor neuron survival in models of spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) and ALS. It has been reported that inhibition of PTEN attenuates the death of hippocampal neurons post injury by decreasing the effective translocation of the GluR2 subunit into the membrane. In addition, leptin can regulate AMPA receptor trafficking via PTEN inhibition. Thus, we speculate that manipulation of AMPA receptors by PTEN may represent a potential therapeutic strategy for neuroprotective intervention in ALS and other neurodegenerative disorders. To this end, the first step is to establish a fibroblast-iPS-motor neuron in vitro cell model to study AMPA receptor manipulation. Here we report that iPS-derived motor neurons from human fibroblasts express AMPA receptors. PTEN depletion decreases AMPA receptor expression and AMPA-mediated whole-cell currents, resulting in inhibition of AMPA-induced neuronal death in primary cultured and iPS-derived motor neurons. Taken together, our results imply that PTEN depletion may protect motor neurons by inhibition of excitatory transmission that represents a therapeutic strategy of potential benefit for the amelioration of excitotoxicity in ALS and other neurodegenerative disorders.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Slow and selective death of spinal motor neurons in vivo by intrathecal infusion of kainic acid: implications for AMPA receptor-mediated excitotoxicity in ALS.J Neurochem. 2006 Aug;98(3):782-91. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.03903.x. J Neurochem. 2006. PMID: 16893420
-
Depalmitoylation preferentially downregulates AMPA induced Ca2+ signaling and neurotoxicity in motor neurons.Brain Res. 2013 Sep 5;1529:143-53. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2013.06.039. Epub 2013 Jul 10. Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 23850769
-
Altered presymptomatic AMPA and cannabinoid receptor trafficking in motor neurons of ALS model mice: implications for excitotoxicity.Eur J Neurosci. 2008 Feb;27(3):572-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06041.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18279310 Free PMC article.
-
Update on the glutamatergic neurotransmitter system and the role of excitotoxicity in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.Muscle Nerve. 2002 Oct;26(4):438-58. doi: 10.1002/mus.10186. Muscle Nerve. 2002. PMID: 12362409 Review.
-
Deficient RNA editing of GluR2 and neuronal death in amyotropic lateral sclerosis.J Mol Med (Berl). 2005 Feb;83(2):110-20. doi: 10.1007/s00109-004-0599-z. Epub 2004 Dec 29. J Mol Med (Berl). 2005. PMID: 15624111 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA-9 Mediates the Cell Apoptosis by Targeting Bcl2l11 in Ischemic Stroke.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Dec;53(10):6809-6817. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9605-4. Epub 2015 Dec 11. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26660116
-
The fused in sarcoma protein forms cytoplasmic aggregates in motor neurons derived from integration-free induced pluripotent stem cells generated from a patient with familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis carrying the FUS-P525L mutation.Neurogenetics. 2015 Jul;16(3):223-31. doi: 10.1007/s10048-015-0448-y. Epub 2015 Apr 26. Neurogenetics. 2015. PMID: 25912081
-
Aberrant Synaptic PTEN in Symptomatic Alzheimer's Patients May Link Synaptic Depression to Network Failure.Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2021 May 11;13:683290. doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2021.683290. eCollection 2021. Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34045952 Free PMC article.
-
Ligand-independent activation of the P2X7 receptor by Hsp90 inhibition stimulates motor neuron apoptosis.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2019 Aug;244(11):901-914. doi: 10.1177/1535370219853798. Epub 2019 May 29. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2019. PMID: 31142143 Free PMC article.
-
[Effects of lentivirus-mediated RNA interference of HIF-1α and PTEN on oxygen-glucose deprivation injury in primary cultured rat neurons].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2021 Dec 20;41(12):1795-1800. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2021.12.06. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2021. PMID: 35012910 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
-
- Rosen DR, Siddique T, Patterson D, Figlewicz DA, Sapp P, Hentati A, et al. Mutations in Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase gene are associated with familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nature. 1993;362:59–62. - PubMed
-
- Gurney ME, Pu H, Chiu AY, Dal Canto MC, Polchow CY, Alexander DD, et al. Motor neuron degeneration in mice that express a human Cu,Zn superoxide dismutase mutation. Science. 1994;264:1772–1775. - PubMed
-
- Pehar M, Vargas MR, Cassina P, Barbeito AG, Beckman JS, Barbeito L. Complexity of astrocyte-motor neuron interactions in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurodegener Dis. 2005;2:139–146. - PubMed
-
- Boillee S, Yamanaka K, Lobsiger CS, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Kassiotis G, et al. Onset and progression in inherited ALS determined by motor neurons and microglia. Science. 2006;312:1389–1392. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

