REV-ERB and ROR nuclear receptors as drug targets
- PMID: 24577401
- PMCID: PMC4865262
- DOI: 10.1038/nrd4100
REV-ERB and ROR nuclear receptors as drug targets
Abstract
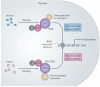
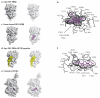
The nuclear receptors REV-ERB (consisting of REV-ERBα and REV-ERBβ) and retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptors (RORs; consisting of RORα, RORβ and RORγ) are involved in many physiological processes, including regulation of metabolism, development and immunity as well as the circadian rhythm. The recent characterization of endogenous ligands for these former orphan nuclear receptors has stimulated the development of synthetic ligands and opened up the possibility of targeting these receptors to treat several diseases, including diabetes, atherosclerosis, autoimmunity and cancer. This Review focuses on the latest developments in ROR and REV-ERB pharmacology indicating that these nuclear receptors are druggable targets and that ligands targeting these receptors may be useful in the treatment of several disorders.
Figures





References
-
- McKenna NJ, Lanz RB, O’Malley BW. Nuclear receptor coregulators: cellular and molecular biology. Endocr. Rev. 1999;20:321–344. - PubMed
-
- Savkur RS, Burris TP. The coactivator LXXLL nuclear receptor recognition motif. J. Pept. Res. 2004;63:207–212. - PubMed
-
- Kliewer SA, Lehmann JM, Willson TM. Orphan nuclear receptors: shifting endocrinology into reverse. Science. 1999;284:757–760. - PubMed
-
- Schulman IG, Heyman RA. The flip side: Identifying small molecule regulators of nuclear receptors. Chem. Biol. 2004;11:639–646. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

