Cardiovascular risk assessment in low-resource settings: a consensus document of the European Society of Hypertension Working Group on Hypertension and Cardiovascular Risk in Low Resource Settings
- PMID: 24577410
- PMCID: PMC3979828
- DOI: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000000125
Cardiovascular risk assessment in low-resource settings: a consensus document of the European Society of Hypertension Working Group on Hypertension and Cardiovascular Risk in Low Resource Settings
Abstract
The Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study 2010 confirms ischemic heart disease and stroke as the leading cause of death and that hypertension is the main associated risk factor worldwide. How best to respond to the rising prevalence of hypertension in resource-deprived settings is a topic of ongoing public-health debate and discussion. In low-income and middle-income countries, socioeconomic inequality and cultural factors play a role both in the development of risk factors and in the access to care. In Europe, cultural barriers and poor communication between health systems and migrants may limit migrants from receiving appropriate prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. To use more efficiently resources available and to make treatment cost-effective at the patient level, cardiovascular risk approach is now recommended. In 2011, The European Society of Hypertension established a Working Group on 'Hypertension and Cardiovascular risk in low resource settings', which brought together cardiologists, diabetologists, nephrologists, clinical trialists, epidemiologists, economists, and other stakeholders to review current strategies for cardiovascular risk assessment in population studies in low-income and middle-income countries, their limitations, possible improvements, and future interests in screening programs. This report summarizes current evidence and presents highlights of unmet needs.
Figures
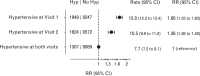
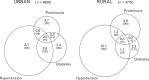
References
-
- Lim SS, Vos T, Flaxman AD, Danaei G, Shibuya K, Adair-Rohani H, et al. A comparative risk assessment of burden of disease and injury attributable to 67 risk factors and risk factor clusters in 21 regions, 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012; 380:2224–2260 - PMC - PubMed
-
- WHO A global brief on Hypertension. Silent killer, global public health crisis. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO; 2013. 40
-
- Ibrahim MM, Damasceno A. Hypertension in developing countries. Lancet 2012; 380:611–619 - PubMed
-
- de Villiers L, Badri M, Ferreira M, Bryer A. Stroke outcomes in a socio-economically disadvantaged urban community. S Afr Med J 2011; 101:345–348 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

