Oxidative stress, T cell DNA methylation, and lupus
- PMID: 24577881
- PMCID: PMC4141415
- DOI: 10.1002/art.38427
Oxidative stress, T cell DNA methylation, and lupus
Abstract
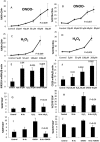
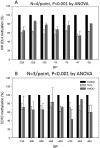
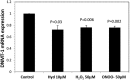
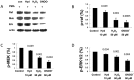
Objective: Lupus develops when genetically predisposed people encounter environmental agents, such as ultraviolet light, silica, infections, and cigarette smoke, that cause oxidative stress, but how oxidative damage modifies the immune system to cause lupus flares is unknown. We previously showed that inhibiting DNA methylation in CD4+ T cells by blocking ERK pathway signaling is sufficient to alter gene expression, and that the modified cells cause lupus-like autoimmunity in mice. We also reported that T cells from patients with active lupus have decreased ERK pathway signaling, have decreased DNA methylation, and overexpress genes normally suppressed by DNA methylation. This study was undertaken to test whether oxidizing agents decrease ERK pathway signaling in T cells, decrease DNA methyltransferase levels, and cause demethylation and overexpression of T cell genes similar to that found in T cells from patients with active lupus.
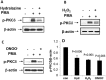
Methods: CD4+ T cells were treated with the oxidizers H2 O2 or ONOO(-) . Effects on ERK pathway signaling were measured by immunoblotting, DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT-1) levels were measured by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), and the methylation and expression of T cell genes were measured using flow cytometry, RT-PCR, and bisulfite sequencing.
Results: H2 O2 and ONOO(-) inhibited ERK pathway signaling in T cells by inhibiting the upstream regulator protein kinase Cδ, decreased DNMT-1 levels, and caused demethylation and overexpression of genes previously shown to be suppressed by DNA methylation in T cells from patients with active lupus.
Conclusion: Our findings indicate that oxidative stress may contribute to human lupus flares by inhibiting ERK pathway signaling in T cells to decrease DNMT-1 and cause DNA demethylation.
© 2014 The Authors. Arthritis & Rheumatology is published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of the American College of Rheumatology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CD4(+) T cells epigenetically modified by oxidative stress cause lupus-like autoimmunity in mice.J Autoimmun. 2015 Aug;62:75-80. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2015.06.004. Epub 2015 Jul 9. J Autoimmun. 2015. PMID: 26165613 Free PMC article.
-
Protein kinase Cδ oxidation contributes to ERK inactivation in lupus T cells.Arthritis Rheum. 2012 Sep;64(9):2964-74. doi: 10.1002/art.34503. Arthritis Rheum. 2012. PMID: 22549474 Free PMC article.
-
The catalytic subunit of protein phosphatase 2A (PP2Ac) promotes DNA hypomethylation by suppressing the phosphorylated mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) kinase (MEK)/phosphorylated ERK/DNMT1 protein pathway in T-cells from controls and systemic lupus erythematosus patients.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jul 26;288(30):21936-44. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.467266. Epub 2013 Jun 17. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23775084 Free PMC article.
-
The interaction between environmental triggers and epigenetics in autoimmunity.Clin Immunol. 2018 Jul;192:1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2018.04.005. Epub 2018 Apr 9. Clin Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29649575 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Key role of ERK pathway signaling in lupus.Autoimmunity. 2010 Feb;43(1):17-22. doi: 10.3109/08916930903374832. Autoimmunity. 2010. PMID: 19961364 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Editorial: LINEing Up to Boost Interferon Production: Activation of Endogenous Retroviral DNA in Autoimmunity.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016 Nov;68(11):2568-2570. doi: 10.1002/art.39794. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 27338170 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Effect of DNA methylation on the osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells: concise review.Front Genet. 2024 Jul 2;15:1429844. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1429844. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 39015772 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic dysregulation of ACE2 and interferon-regulated genes might suggest increased COVID-19 susceptibility and severity in lupus patients.Clin Immunol. 2020 Jun;215:108410. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2020.108410. Epub 2020 Apr 8. Clin Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32276140 Free PMC article.
-
Dose- and time- effect responses of DNA methylation and histone H3K9 acetylation changes induced by traffic-related air pollution.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 3;7:43737. doi: 10.1038/srep43737. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28256616 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Oxidative Stress in Epigenetic Changes Underlying Autoimmunity.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2022 Mar;36(7-9):423-440. doi: 10.1089/ars.2021.0066. Epub 2022 Jan 4. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2022. PMID: 34544258 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bogdanos DP, Smyk DS, Rigopoulou EI, Mytilinaiou MG, Heneghan MA, Selmi C, et al. Twin studies in autoimmune disease: genetics, gender and environment. J Autoimmun. 2012;38:J156–69. - PubMed
-
- Richardson B. Primer: epigenetics of autoimmunity. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2007;3:521–7. - PubMed
-
- Zandman-Goddard G, Solomon M, Rosman Z, Peeva E, Shoenfeld Y. Environment and lupus-related diseases. Lupus. 2012;21:241–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

