Tocolytics for preterm premature rupture of membranes
- PMID: 24578236
- PMCID: PMC11194776
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD007062.pub3
Tocolytics for preterm premature rupture of membranes
Abstract
Background: In women with preterm labor, tocolysis has not been shown to improve perinatal mortality; however, it is often given for 48 hours to allow for the corticosteroid effect for fetal maturation. In women with preterm premature rupture of membranes (PPROM), the use of tocolysis is still controversial. In theory, tocolysis may prolong pregnancy in women with PPROM, thereby allowing for the corticosteroid benefit and reducing the morbidity and mortality associated with prematurity.
Objectives: To assess the potential benefits and harms of tocolysis in women with preterm premature rupture of membranes.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group's Trials Register (15 January 2014).
Selection criteria: We included pregnant women with singleton pregnancies and PPROM (23 weeks to 36 weeks and six days). We included any tocolytic therapy compared to no tocolytic, placebo, or another tocolytic.
Data collection and analysis: All review authors assessed the studies for inclusion. We extracted and quality assessed data.
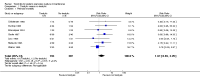
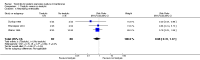
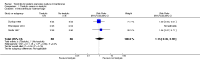
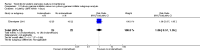
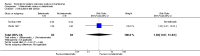
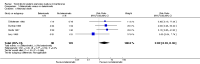
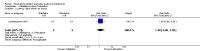
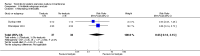
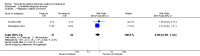
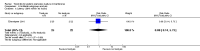
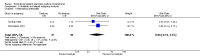
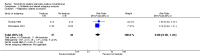
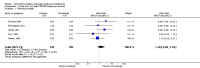
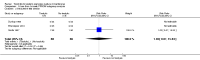
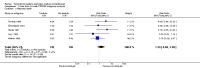
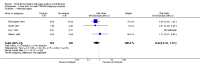
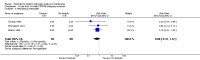
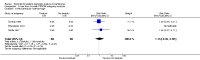
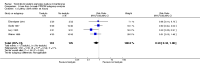
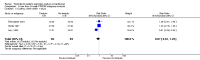
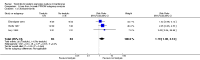
Main results: We included eight studies with a total of 408 women. Seven of the studies compared tocolysis to no tocolysis. One study compared nifedipine to terbutaline. Compared to no tocolysis, tocolysis was not associated with a significant effect on perinatal mortality in women with PPROM (risk ratio (RR) 1.67; 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.85 to 3.29). Tocolysis was associated with longer latency (mean difference (MD) 73.12 hours; 95% CI 20.21 to 126.03; three trials of 198 women) and fewer births within 48 hours (average RR 0.55; 95% CI 0.32 to 0.95; six trials of 354 women; random-effects, Tau² = 0.18, I² = 43%) compared to no tocolysis. However, tocolysis was associated with increased five-minute Apgar of less than seven (RR 6.05; 95% CI 1.65 to 22.23; two trials of 160 women) and increased need for ventilation of the neonate (RR 2.46; 95% CI 1.14 to 5.34; one trial of 81 women). In the subgroup analysis comparing betamimetic to no betamimetics, tocolysis was associated with increased latency and borderline significance for chorioamnionitis. Prophylactic tocolysis with PPROM was associated with increased overall latency, without additional benefits for maternal/neonatal outcomes. For women with PPROM before 34 weeks, there was a significantly increased risk of chorioamnionitis in women who received tocolysis. However, neonatal outcomes were not significantly different. There were no significant differences in maternal/neonatal outcomes in subgroup analyses comparing cox inhibitor versus no tocolysis, calcium channel blocker versus betamimetic, antibiotic, corticosteroid or combined antibiotic/corticosteroid.
Authors' conclusions: Our review suggests there is insufficient evidence to support tocolytic therapy for women with PPROM, as there was an increase in maternal chorioamnionitis without significant benefits to the infant. However, studies did not consistently administer latency antibiotics and corticosteroids, both of which are now considered standard of care.
Conflict of interest statement
None known.
Figures



















































































Update of
-
Tocolytics for preterm premature rupture of membranes.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Oct 5;(10):CD007062. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007062.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Feb 27;(2):CD007062. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007062.pub3. PMID: 21975760 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Christensen 1980 {published data only}
-
- Christensen K, Ingemarsson I, Leideman T, Solum H, Svenningesen N. Effect of ritodrine on labor after premature rupture of membranes. Obstetrics & Gynecology 1980;55(2):187‐90. - PubMed
Dunlop 1986 {published data only}
-
- Dunlop P, Crowley P, Lamont R, Hawkins D. Preterm ruptured membranes, no contractions. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 1986;7:92‐6.
Ehansipoor 2010 {published data only}
-
- Ehsanipoor RM, Shrivastava VK, Lee RM, Chan K, Galyean AM, Garite TJ, et al. A randomized, double‐masked trial of prophylactic indomethacin tocolysis versus placebo in women with premature rupture of membranes. American Journal of Perinatology 2010 Dec 17 [Epub ahead of print]. [PUBMED: 21170827] - PubMed
Garite 1987 {published data only}
-
- Garite T, Keegan K, Freeman R, Nageotte M. A randomised trial of ritodrine tocolysis versus expectant management in patients with premature rupture of membranes at 25 to 30 weeks of gestation. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1987;157(2):388‐93. - PubMed
Laohapojanart 2007 {published data only}
-
- Laohapojanart N, Soorapan S, Wacharaprechanont T, Ratanajamit C. Safety and efficacy of oral nifedipine versus terbutaline injection in preterm labor. Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand 2007;90:2461‐9. - PubMed
Levy 1985 {published data only}
-
- Levy D, Warsof S. Oral ritodrine and preterm premature rupture of membranes. Obstetrics & Gynecology 1985;66:621‐3. - PubMed
Matsuda 1993 {published data only}
-
- Matsuda Y, Ikenoue K, Ibara S, Sameshima H, Kuraya K, Hokanishi H. The efficacy of prophylactic antibiotic and tocolytic therapy for premature rupture of the membranes ‐ a prospective randomized study. Acta Obstetrica et Gynaecologica Japonica 1993;45:1109‐14. - PubMed
-
- Matsuda Y, Ikenoue T, Hokanishi H. Premature rupture of the membranes‐aggressive vs conservative approach: effect of tocolytic and antibiotic therapy. Gynecologic and Obstetric Investigation 1993;36:102‐7. - PubMed
-
- Matsuda Y, Nakamura Y, Asano H, Hirano T, Sameshima H, Ibara S, et al. Premature rupture of the membranes and infectious outcome. Journal of Perinatal Medicine 1991;19(Suppl 2):248.
Weiner 1988 {published data only}
-
- Weiner C, Renk K, Klugman M. The therapeutic efficacy and cost‐effectiveness of aggressive tocolysis for premature labor associated with premature rupture of membranes. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1988;159:216‐22. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Bisits 2004 {published data only}
-
- Bisits A, Madsen M, Knox A, Gill A, Smith R, Yeo G, et al. The randomised nitric oxide tocolysis trial (RNOTT) for the treatment of preterm labor. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2004;191:683‐90. - PubMed
Briery 2009 {published data only}
-
- Briery C, Veillon E, Klauser CK, Martin R, Chauhan S, Magann EF, et al. Women with prolonged premature rupture of the membrane do not benefit from weekly progesterone: a randomized clinical trial. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2009;201(6 Suppl 1):S189. - PubMed
Caritis 1982 {published data only}
-
- Caritis S, Carson D, Greebon D, McCormick M, Edelstone D, Mueller‐Heubach E. A comparison of terbutaline and ethanol in the treatment of preterm labor. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1982;142:183‐90. - PubMed
Caritis 1984 {published data only}
-
- Caritis S, Toig G, Heddinger L, Ashmead G. A double‐blind study comparing ritodrine and terbutaline in the treatment of preterm labor. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1984;150:7‐14. - PubMed
Cotton 1984 {published data only}
-
- Cotton DB, Strassner HT, Hill LM, Schifrin BS, Paul RH. Comparison of magnesium sulfate, terbutaline and a placebo for inhibition of preterm labor. A randomised study. Journal of Reproductive Medicine 1984;29:92‐7. - PubMed
Decavalas 1995 {published data only}
-
- Decavalas G, Mastrogiannis D, Papadopoulos V, Tzingounis V. Short‐term versus long‐term prophylactic tocolysis in patients with preterm premature rupture of membranes. European Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1995;59:143‐7. - PubMed
-
- Decavalas G, Papadopoulos V, Tsapanos V, Tzingounis V. Tocolysis inpatients with preterm premature rupture of membranes has any effect on pregnancy outcome?. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 1994;46:26.
El‐Sayed 1999 {published data only}
-
- El‐Sayed YY, Riley ET, Holbrook RH Jr, Cohen SE, Chitkara U, Druzin ML. Randomized comparison of intravenous nitroglycerin and magnesium sulfate for treatment of preterm labor. Obstetrics & Gyneoclogy 1999;93:79‐83. - PubMed
Essed 1978 {published data only}
-
- Essed GGM, Eskes TKAB, Jongsma HW. A randomised trial of two beta‐mimetic drugs for the treatment of threatening early labor. Clinical results in a prospective comparative study with ritodrine and fenoterol European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology;148:341‐8.
Ferguson 1984 {published data only}
-
- Ferguson JE II, Holbrook H, Stevenson DK, Hensleigh PA, Kredenster D. Adjuntive magnesium sulfate infusion does not alter metabolic changes associated with ritodrine tocolysis. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1987;156:103‐7. - PubMed
-
- Ferguson JE, Hensleigh PA, Kredenster D. Adjunctive use of magnesium sulfate with ritodrine for preterm labor. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1984;148:166‐71. - PubMed
Ferguson 1989 {published data only}
-
- Ferguson JE II, Dyson DC, Holbrook H, Schutz T, Stevenson DK. Cardiovascular and metabolic effects associated with nifedipine and ritodrine tocolysis. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1989;161:788‐95. - PubMed
-
- Ferguson JE, Dyson DC, Schultz T, Stevenson DK. A comparison of tocolysis with nifedipine or ritodrine: analysis of efficacy and maternal, fetal, and neonatal outcome. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1990;163:105‐11. - PubMed
-
- Ferguson JE, Schultz TE, Stevenson DK. Neonatal bilirubin production after pre‐term labor tocolysis with nifedipine. Developmental Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1989;12:113‐7. - PubMed
Freeman 2008 {published data only}
-
- Freeman B, Elliott J. Tocolytic therapy in preterm rupture of membranes. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2008;199:S84.
Gamissans 1982 {published data only}
-
- Gamissans O, Balasch J. Prostaglandin synthetase inhibitors in the treatment of preterm labor. Preterm Birth: Causes, Prevention and Management. New York: Macmillan, 1984:223‐48.
-
- Gamissans O, Cararach V, Serra J. The role of prostaglandin‐inhibitors, beta‐adrenergic drugs and glucocorticoids in the management of threatened preterm labor. Beta‐mimetic drugs in obstetrics and perinatology. 3rd Symposium on beta‐mimetic drugs; November 1980. Aachen. Stuttgard: Georg Thieme, 1982:71‐84.
Gill 2006 {published data only}
-
- Gill A, Madsen G, Knox M, Bisits A, Giles W, Tudehope D, et al. Neonatal neurodevelopmental outcomes following tocolysis with glycerol trinitrate patches. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2006;195(2):484‐7. - PubMed
-
- Gill A, Madsen G, Knox M, Bisits A, Giles W, Tudehope D, et al. Neonatal neurodevelopmental outcomes following tocolysis with glycerol trinitrate patches and IV beta 2 agonist therapy. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2002;187:S117. - PubMed
Holleboom 1996 {published data only}
-
- Holleboom CAG, Merkus JMWM, Elferen LWM, Keirse MJNC. Randomised comparison between a loading and incremental dose model for ritodrine administration in preterm labour. British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 1996;103:695‐701. - PubMed
Houtzager 2006 {published data only}
-
- Houtzager BA, Hogendoorn S, Samson JF, Papatsonis D, Wassenaer AG. Nine years' follow up of children born from mothers who participated in a RCT of nifedipine versus ritodrine for threatened preterm labor. Pediatric Academic Societies Annual Meeting; 2005 May 14‐17; Washington DC, USA. Pediatric Academic Society, 2005:Abstract no: 2100.
-
- Houtzager BA, Hogendoorn SM, Papatsonis DN, Samsom JF, Geijn HP, Bleker OP, et al. Long‐term follow‐up of children exposed in utero to nifedipine or ritodrine for the management of preterm labour. BJOG: an international journal of obstetrics and gynaecology 2006;113:324‐31. - PubMed
How 1998 {published data only}
-
- How H, Cook C, Cook V, Miles D, Spinnato J. Preterm premature rupture of membranes aggressive tocolysis versus expectant management. Journal of Maternal‐Fetal Medicine 1998;7:8‐12. - PubMed
-
- How H, Cook C, Cook V, Spinnato J. Preterm premature rupture of membranes: aggressive tocolysis versus expectant management. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1996;174:306. - PubMed
Husslein 2007 {published data only}
-
- Husslein P, Roura L, Dudenhausen J, Helmer H, Frydman R, Rizzo N, et al. Atosiban versus usual care for the management of preterm labor. Journal of Perinatal Medicine 2007;35:305‐13. - PubMed
Ingemarsson 1976 {published data only}
-
- Ingemarsson I. Effect of terbutaline on premature labor. A double‐blind placebo controlled study. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1976;125:520‐4. - PubMed
Kashanian 2005 {published data only}
-
- Kashanian M, Akbarian AR, Soltanzadeh M. Atosiban and nifedipine for the treatment of preterm labor. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 2005;91:10‐4. - PubMed
Katz 1983 {published data only}
-
- Katz J, Lancet M, Yemini M, Mogilner BM, Feigl A, Ben‐Hur H. Treatment of premature labor contractions with combined ritodrine and indomethacin. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 1983;21:337‐42. - PubMed
Koks 1998 {published data only}
-
- Koks C, Brolmann H, Kleine M, Manger P. A randomised comparison of nifedipine and ritodrine for suppression of preterm labor. European Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1998;77:171‐6. - PubMed
Leake 1983 {published data only}
-
- Leake RD, Hobel CJ, Oh W, Thibeault DW, Okada DM, Williams PR. A controlled, prospective study of the effect of ritodrine hydrochloride for premature labor. Clinical Research 1980;28:90A.
-
- Leake RD, Hobel CJ, Oh W, Thibeault DW, Okada DM, Williams PR. A controlled, prospective study of the effect of ritodrine hydrochloride for premature labor. Pediatric Research 1980;14:603.
-
- Leake RD, Hobel CJ, Okada DM, Ross MG, Williams PR. Neonatal metabolic effects of oral ritodrine hydrochloride administration. Pediatric Pharmocology 1983;3:101‐6. - PubMed
Lyell 2007 {published data only}
-
- Lyell D, Pullen K, Campbell L, Ching S, Burrs D, Chitkara U, et al. Magnesium sulfate versus nifedipine for acute tocolysis of preterm labor. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2005;193:s18. - PubMed
-
- Lyell D, Pullen K, Campbell L, Ching S, Druzin M, Chikara U, et al. Magnesium sulfate compared with nifedipine for acute tocolysis of preterm labor. Obstetrics & Gynecology 2007;1:61‐7. - PubMed
Mittendorf 1997 {published data only}
-
- Mittendorf R, Bentz L, Borg M, Roizen N. Does exposure to antenatal magnesium sulfate prevent cerebral palsy. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2000;182:S20.
-
- Mittendorf R, Covert R, Boman J, Khoshnood B, Lee KS, Siegler M. Is tocolytic magnesium sulphate associated with increased paediatric mortality. Lancet 1997;350:1517‐8. - PubMed
-
- Mittendorf R, Covert R, Elin R, Pryde P, Khoshnood B, Lee KS. Umbilical cord serum ionized magnesium level and total paediatric mortality. Obstetrics & Gynecology 2001;98:75‐8. - PubMed
-
- Mittendorf R, Dambrosia J, Khoshnood B, Lee KS, Pryde P, Yousefzadeh D. Association between magnesium and intraventricular haemorrhage. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2001;184:S188.
-
- Mittendorf R, Dambrosia J, Khoshnood B, Lee KS, Pryde P, Yousefzadeh D. Magnesium sulfate is no more efficacious than other tocolytic agents. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2002;184(1):S188.
Moutquin 1992 {published data only}
-
- Sauve RS. Outcomes of ritodrine exposed infants. Pediatric Research 1991;29:264A.
-
- The Canadian Preterm Labor Investigator Group. Treatment of preterm labor with the beta‐adrenergic agonist ritodrine. The New England Journal of Medicine 1992;327:308‐12. - PubMed
Nelson 1985 {published data only}
-
- Nelson L, Meis P, Hatjis C, Ernest J, Dillard R, Schey H. Premature rupture of membranes: a prospective, randomised evaluation of steroids, latent phase and expectant management. Obstetrics & Gynecology 1985;66:55‐8. - PubMed
Papatsonis 1997 {published data only}
-
- Papatsonis D, Kok J, Geijn H, Bleker O, Ader H, Dekker G. Neonatal effects of nifedipine and ritodrine for preterm labor. Obstetrics and Gynecology 2000;95:477‐481. - PubMed
-
- Papatsonis D, Geijn V, Ader H, Lange F, Bleker O, Dekker G. Nifedipine and ritodrine in the management of preterm labor: a randomised multicenter trial. Obstetrics & Gynecology 1997;90(2):230‐4. - PubMed
-
- Papatsonis DN, Geign HP, Dekker GA. Nifedipine as a safe and effective tocolytic agent in the treatment of preterm labor. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2000;183:513‐4. - PubMed
-
- Papatsonis DN, Geijn HP, Bleker OP, Ader HJ, Dekker GA. Hemodynamic and metabolic effects after nifedipine and ritodrine tocolysis. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 2003;82:513‐4. - PubMed
-
- Papatsonis DNM, Hogedoorn SM, Houtzager BA, Wassenaer AG, Samsom JF. Long‐term follow‐up of children exposed in utero to nifedipine or ritodrine in the management of preterm labor. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2004;191(6 Suppl 1):S106. - PubMed
Parsons 1988 {published data only}
-
- Parsons MT, Sobel D, Cummiskey K, Constantine L, Roitman J. Steroid, antibiotic and tocolytic vs. no steroid, antibiotic and tocolytic management in patients with preterm PPROM at 25‐32 weeks. Proceedings of 8th Annual Meeting of the Society of Perinatal Obstetricians; 1988 Feb 3‐6; Las Vegas, Nevada, USA. 1988:44.
Renzo 2003 {published data only}
-
- Renzo DGC, Mignosa MM, Rosati A, Burnelli L, Epicoco G, Luzi G. Can we effectively arrest premature labour in women with multiple gestations or other high‐risk factors?. 4th World Congress on Controversies in Obstetrics, Gynecology & Infertility; 2003 April 24‐7; Berlin, Germany. 2003:286‐90.
Sims 1978 {published data only}
-
- Sims C, Chamberlain G, Boyd I, Lewis P. A comparison of salbutamol and ethanol in the treatment of preterm labor. British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1978;85:761‐6. - PubMed
Spearing 1979 {published data only}
-
- Spearing G. Alcohol, indomethacin and salbutamol. Obstetrics & Gynecology 1979;2:171‐4. - PubMed
Spellacy 1979 {published data only}
-
- Spellacy W, Cruz A, Birk S, Buhi W. Treatment of premature labor with ritodrine: a randomised controlled trial. Obstetrics & Gynecology 1979;54:220‐3. - PubMed
Tchilinguirian 1984 {published data only}
-
- Tchilinguirian NG, Najem R, Sullivan GB, Craparo FJ. The use of ritodrine and magnesium sulfate in the arrest of premature labor. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 1984;22:117‐23. - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
El‐Sayed 2010 {published data only}
-
- El‐Sayed YY. Progesterone for the management of preterm, premature rupture of the membranes: a randomized controlled trial. ClinicalTrials.gov (accessed 21 May 2013) 2010.
Mol 2012 {published data only}
-
- Mol B. Assessment of Perinatal Outcome by uSe of Tocolysis in Early Labour: Nifedipine versus placebo in the treatment of preterm premature rupture of membranes. Netherlands Trials Register (http://www.trialregister.nl) (accessed 3 November 2012) 2012.
Additional references
ACOG 2007
-
- Mercer B, for the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Premature rupture of membranes. Obstetrics & Gynecology 2007;109:1007‐19. - PubMed
Anotayanonth 2004
Crowther 2002
Crowther 2007
Harding 2001
-
- Harding JE, Pang J, Knight DB, Liggins GC. Do antenatal corticosteroids help in the setting of preterm rupture of membranes?. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2001;184:131‐9. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Kaltreider 1980
-
- Kaltreider DF, Kohl S. Epidemiology of preterm delivery. Clinical Obstetrics and Gynecology 1980;23(1):17‐31. - PubMed
Kenyon 2001
-
- Kenyon SL, Taylor DJ, Tarnow‐Mordi W, for the ORACLE Collaborative Group. Broad‐spectrum antibiotics for preterm, prelabour rupture of fetal membranes: the ORACLE 1 randomised trial. Lancet 2001;357:979‐88. - PubMed
Kenyon 2003
King 2000
King 2003
King 2005
Mercer 1995
-
- Mercer B, Arheart K. Antimicrobial therapy in expectant management of preterm premature rupture of the membranes. Lancet 1995;346:1271‐9. - PubMed
Ohlsson 2009
Papatsonis 2005
Parry 1998
-
- Parry S, Strauss JF 3rd. Premature rupture of the fetal membranes. New England Journal of Medicine 1998;338(10):663‐70. - PubMed
RevMan 2011 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.1. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011.
Roberts 2006
Shatrov 2010
-
- Shatrov JG, Birch SC, Lam LT, Quinlivan JA, McIntyre S, Mendz GL. Chorioamnionitis and cerebral palsy: a meta‐analysis. Obstetrics & Gynecology 2010;116(2 Pt 1):387‐92. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

