Divergent roles for maize PAN1 and PAN2 receptor-like proteins in cytokinesis and cell morphogenesis
- PMID: 24578508
- PMCID: PMC3982752
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.113.232660
Divergent roles for maize PAN1 and PAN2 receptor-like proteins in cytokinesis and cell morphogenesis
Abstract
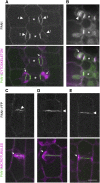
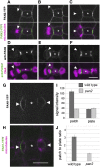
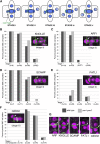
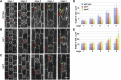
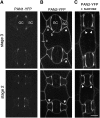
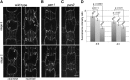
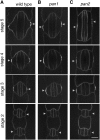
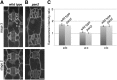
Pangloss1 (PAN1) and PAN2 are leucine-rich repeat receptor-like proteins that function cooperatively to polarize the divisions of subsidiary mother cells (SMCs) during stomatal development in maize (Zea mays). PANs colocalize in SMCs, and both PAN1 and PAN2 promote polarization of the actin cytoskeleton and nuclei in these cells. Here, we show that PAN1 and PAN2 have additional functions that are unequal or divergent. PAN1, but not PAN2, is localized to cell plates in all classes of dividing cells examined. pan1 mutants exhibited no defects in cell plate formation or in the recruitment or removal of a variety of cell plate components; thus, they did not demonstrate a function for PAN1 in cytokinesis. PAN2, in turn, plays a greater role than PAN1 in directing patterns of postmitotic cell expansion that determine the shapes of mature stomatal subsidiary cells and interstomatal cells. Localization studies indicate that PAN2 impacts subsidiary cell shape indirectly by stimulating localized cortical actin accumulation and polarized growth in interstomatal cells. Localization of PAN1, Rho of Plants2, and PIN1a suggests that PAN2-dependent cell shape changes do not involve any of these proteins, indicating that PAN2 function is linked to actin polymerization by a different mechanism in interstomatal cells compared with SMCs. Together, these results demonstrate that PAN1 and PAN2 are not dedicated to SMC polarization but instead play broader roles in plant development. We speculate that PANs may function in all contexts to regulate polarized membrane trafficking either directly or indirectly via their influence on actin polymerization.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The intracellular and intercellular cross-talk during subsidiary cell formation in Zea mays: existing and novel components orchestrating cell polarization and asymmetric division.Ann Bot. 2018 Nov 3;122(5):679-696. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcx193. Ann Bot. 2018. PMID: 29346521 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of PAN2 by quantitative proteomics as a leucine-rich repeat-receptor-like kinase acting upstream of PAN1 to polarize cell division in maize.Plant Cell. 2012 Nov;24(11):4577-89. doi: 10.1105/tpc.112.104125. Epub 2012 Nov 21. Plant Cell. 2012. PMID: 23175742 Free PMC article.
-
ROP GTPases act with the receptor-like protein PAN1 to polarize asymmetric cell division in maize.Plant Cell. 2011 Jun;23(6):2273-84. doi: 10.1105/tpc.111.085597. Epub 2011 Jun 7. Plant Cell. 2011. PMID: 21653193 Free PMC article.
-
PAN1: a receptor-like protein that promotes polarization of an asymmetric cell division in maize.Science. 2009 Jan 30;323(5914):649-51. doi: 10.1126/science.1161686. Science. 2009. PMID: 19179535
-
The role of the cytoskeleton and associated proteins in determination of the plant cell division plane.Plant J. 2013 Jul;75(2):258-69. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12177. Epub 2013 Apr 19. Plant J. 2013. PMID: 23496276 Review.
Cited by
-
Subcellular positioning during cell division and cell plate formation in maize.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Jul 7;14:1204889. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1204889. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37484472 Free PMC article.
-
The intracellular and intercellular cross-talk during subsidiary cell formation in Zea mays: existing and novel components orchestrating cell polarization and asymmetric division.Ann Bot. 2018 Nov 3;122(5):679-696. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcx193. Ann Bot. 2018. PMID: 29346521 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Auxin as an inducer of asymmetrical division generating the subsidiary cells in stomatal complexes of Zea mays.Plant Signal Behav. 2015;10(3):e984531. doi: 10.4161/15592324.2014.984531. Plant Signal Behav. 2015. PMID: 25831267 Free PMC article.
-
Asymmetric cell division in plants: mechanisms of symmetry breaking and cell fate determination.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016 Nov;73(22):4213-4229. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2290-2. Epub 2016 Jun 10. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 27286799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic N-glycoproteome analysis of maize seedling leaves during de-etiolation using Concanavalin A lectin affinity chromatography and a nano-LC-MS/MS-based iTRAQ approach.Plant Cell Rep. 2017 Dec;36(12):1943-1958. doi: 10.1007/s00299-017-2209-x. Epub 2017 Sep 23. Plant Cell Rep. 2017. PMID: 28942497
References
-
- Boudeau J, Miranda-Saavedra D, Barton GJ, Alessi DR. (2006) Emerging roles of pseudokinases. Trends Cell Biol 16: 443–452 - PubMed
-
- Cartwright HN, Humphries JA, Smith LG. (2009) PAN1: a receptor-like protein that promotes polarization of an asymmetric cell division in maize. Science 323: 649–651 - PubMed
-
- Castells E, Casacuberta JM. (2007) Signalling through kinase-defective domains: the prevalence of atypical receptor-like kinases in plants. J Exp Bot 58: 3503–3511 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

