Pleuroparenchymal Fibroelastosis: Its Clinical Characteristics
- PMID: 24578677
- PMCID: PMC3933942
- DOI: 10.2174/1573398X0904140129125307
Pleuroparenchymal Fibroelastosis: Its Clinical Characteristics
Abstract
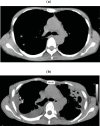
Pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis (PPFE) is a rare pulmonary fibrosis that is clinically characterized by upperlobe predominant fibrosis. PPFE is a slowly progressive disorder and its first symptom is dyspnea or dry cough. Chest pain because of pneumothorax may be the first symptom in some patients. Patients with PPFE are slender with a flat rib cage or abnormally narrowed anterior-posterior thoracic dimension. Decreases in forced vital capacity, total lung capacity, and diffusing capacity are respiratory-function characteristics of PPFE, similar to those seen in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). The most remarkable difference in clinical features between PPFE and IPF is imaging findings, with upper-lobe-predominant lesions in PPFE and lower-lobe-predominant lesions in IPF.
Keywords: Pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis (PPFE); pulmonary fibrosis (IPF).; pulmonary upper lobe fibrosis.
Figures




References
-
- Frankel SK, Cool CD, Lynch DA, Brown KK. Idiopathic pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis.Description of a novel clinicopathologic Entity. . Chest. 2004;126:2007–13. - PubMed
-
- Davies D. Ankylosing spondylitis and lung fibrosis. Q J Med. 1972;41:395–417. - PubMed
-
- Clinicopathological Conference Undiagnosable lung disease demonstrated at the postgraduate medical school of London. Br Med J. 1962;1:1403–10. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
