Impact of learners on emergency medicine attending physician productivity
- PMID: 24578767
- PMCID: PMC3935787
- DOI: 10.5811/westjem.2013.7.15882
Impact of learners on emergency medicine attending physician productivity
Abstract
Introduction: Several prior studies have examined the impact of learners (medical students or residents) on overall emergency department (ED) flow as well as the impact of resident training level on the number of patients seen by residents per hour. No study to date has specifically examined the impact of learners on emergency medicine (EM) attending physician productivity, with regards to patients per hour (PPH). We sought to evaluate whether learners increase, decrease, or have no effect on the productivity of EM attending physicians in a teaching program with one student or resident per attending.
Methods: This was a retrospective database review of an urban, academic tertiary care center with 3 separate teams on the acute care side of the ED. Each team was staffed with one attending physician paired with either one resident, one medical student or with no learners. All shifts from July 1, 2008 to June 30, 2010 were reviewed using an electronic database. We predefined a shift as "Resident" if > 5 patients were seen by a resident, "Medical Student" if any patients were seen by a medical student, and "No Learners" if no patients were seen by a medical student or resident. Shifts were removed from analysis if more than one learner saw patients during the shift. We further stratified resident shifts by EM training level or off-service rotator. For each type of shift, the total number of patients seen by the attending physician was then divided by 8 hours (shift duration) to arrive at number of patients per hour.
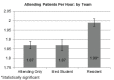
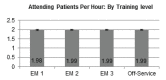
Results: We analyzed a total of 7,360 shifts with 2,778 removed due to multiple learners on a team. For the 2,199 shifts with attending physicians with no learners, the average number of PPH was 1.87(95% confidence interval [CI] 1.86,1.89). For the 514 medical student shifts, the average PPH was 1.87(95% CI 1.84,1.90), p = 0.99 compared with attending with no learner. For the 1,935 resident shifts, the average PPH was 1.99(95% CI 1.97,2.00). Compared with attending physician with no learner, attending physicians with a resident saw more PPH (1.99 vs 1.87, p<0.005). There was no statistically significant difference found between EM1: 1.98PPH, EM2: 1.99PPH, EM3: 1.99PPH, and off-service rotators: 1.99PPH.
Conclusion: EM attending physicians paired with a resident in a one-on-one teaching model saw statistically significantly more patients per hour (0.12 more patients per hour) than EM attending physicians alone. EM attending physicians paired with a medical student saw the same number of patients per hour compared with working alone.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Describing resident physician productivity in a Canadian academic emergency department.CJEM. 2024 Dec;26(12):890-896. doi: 10.1007/s43678-024-00781-6. Epub 2024 Sep 27. CJEM. 2024. PMID: 39333354
-
The impact of the demand for clinical productivity on student teaching in academic emergency departments.Acad Emerg Med. 2004 Dec;11(12):1364-7. doi: 10.1197/j.aem.2004.07.015. Acad Emerg Med. 2004. PMID: 15576531
-
Evaluating the effect of emergency residency training on productivity in the emergency department.J Emerg Med. 2013 Sep;45(3):414-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jemermed.2013.03.022. Epub 2013 Jul 10. J Emerg Med. 2013. PMID: 23849363
-
Call to action: equity, diversity, and inclusion in emergency medicine resident physician selection.CJEM. 2023 Jul;25(7):550-557. doi: 10.1007/s43678-023-00528-9. Epub 2023 Jun 27. CJEM. 2023. PMID: 37368231 Review.
-
Impact of Medical Trainees on Efficiency and Productivity in the Emergency Department: Systematic Review and Narrative Synthesis.West J Emerg Med. 2024 Sep;25(5):767-776. doi: 10.5811/westjem.18574. West J Emerg Med. 2024. PMID: 39319808 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Medical students and metrics: seven techniques for a win-win situation.Int J Emerg Med. 2019 May 6;12(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s12245-019-0230-2. Int J Emerg Med. 2019. PMID: 31179935 Free PMC article.
-
The contribution of resident physicians to hospital productivity.Eur J Health Econ. 2022 Mar;23(2):301-312. doi: 10.1007/s10198-021-01368-z. Epub 2021 Aug 21. Eur J Health Econ. 2022. PMID: 34417903 Free PMC article.
-
Key High-efficiency Practices of Emergency Department Providers: A Mixed-methods Study.Acad Emerg Med. 2018 Jul;25(7):795-803. doi: 10.1111/acem.13361. Epub 2018 Jan 22. Acad Emerg Med. 2018. PMID: 29265539 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Medical Student Involvement on Emergency Department Outcomes: A Tertiary Center Analysis.West J Emerg Med. 2025 Jul 8;26(4):773-780. doi: 10.5811/westjem.42229. West J Emerg Med. 2025. PMID: 40795011 Free PMC article.
-
Productivity, efficiency, and overall performance comparisons between attendings working solo versus attendings working with residents staffing models in an emergency department: A Large-Scale Retrospective Observational Study.PLoS One. 2020 Feb 5;15(2):e0228719. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228719. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32023302 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dowd MD, Tarantino C, Barnett TM, et al. Resident efficacy in a pediatric emergency department. Acad Emerg Med. 2005;12(12):1240–1244. - PubMed
-
- Thibodeau LG, Geary SP, Werter C. An evaluation of resident work profiles, attending-resident teaching interactions, and the effect of variations in emergency department volume on each. Acad Emerg Med. 2010;17(Suppl 2):S62–66. - PubMed
-
- Lammers RL, Roiger M, Rice L, et al. The Effect of a New Emergency Medicine Residency Program on Patient Length of Stay in a Community Hospital Emergency Department. Acad Emerg Med. 2003;10(7):725–730. - PubMed
-
- Chan L, Kass LE. Impact of Medical student preceptorship on ED patient throughput time. Am J Emerg Med. 1999;17:41–43. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

