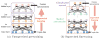Deep learning-based feature representation for AD/MCI classification
- PMID: 24579188
- PMCID: PMC4029347
- DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-40763-5_72
Deep learning-based feature representation for AD/MCI classification
Abstract
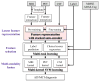
In recent years, there has been a great interest in computer-aided diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease (AD) and its prodromal stage, Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI). Unlike the previous methods that consider simple low-level features such as gray matter tissue volumes from MRI, mean signal intensities from PET, in this paper, we propose a deep learning-based feature representation with a stacked auto-encoder. We believe that there exist latent complicated patterns, e.g., non-linear relations, inherent in the low-level features. Combining latent information with the original low-level features helps build a robust model for AD/MCI classification with high diagnostic accuracy. Using the ADNI dataset, we conducted experiments showing that the proposed method is 95.9%, 85.0%, and 75.8% accurate for AD, MCI, and MCI-converter diagnosis, respectively.
Figures
References
-
- Alzheimer’s Association. Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s & Dementia. 2012;8(2):131–168. - PubMed
-
- Bengio Y. Learning deep architectures for AI. Foundations and Trends in Machine Learning. 2009;2(1):1–127.
-
- Gönen M, Alpaydin E. Multiple kernel learning algorithms. Journal of Machine Learning Research. 2011;12:2211–2268.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical