Long-term effects of chromatin remodeling and DNA damage in stem cells induced by environmental and dietary agents
- PMID: 24579784
- PMCID: PMC3998679
- DOI: 10.1615/jenvironpatholtoxicoloncol.2013007980
Long-term effects of chromatin remodeling and DNA damage in stem cells induced by environmental and dietary agents
Abstract
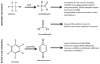
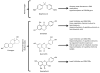
The presence of histones acts as a barrier to protein access; thus chromatin remodeling must occur for essential processes such as transcription and replication. In conjunction with histone modifications, DNA methylation plays critical roles in gene silencing through chromatin remodeling. Chromatin remodeling is also interconnected with the DNA damage response, maintenance of stem cell properties, and cell differentiation programs. Chromatin modifications have increasingly been shown to produce long-lasting alterations in chromatin structure and transcription. Recent studies have shown environmental exposures in utero have the potential to alter normal developmental signaling networks, physiologic responses, and disease susceptibility later in life during a process known as developmental reprogramming. In this review we discuss the long-term impact of exposure to environmental compounds, the chromatin modifications that they induce, and the differentiation and developmental programs of multiple stem and progenitor cell types altered by exposure. The main focus is to highlight agents present in the human lifestyle that have the potential to promote epigenetic changes that impact developmental programs of specific cell types, may promote tumorigenesis through altering epigenetic marks, and may be transgenerational, for example, those able to be transmitted through multiple cell divisions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors and epigenetic modifications as a novel strategy in renal cell carcinoma.Cancer J. 2013 Jul-Aug;19(4):333-40. doi: 10.1097/PPO.0b013e3182a09e07. Cancer J. 2013. PMID: 23867515 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic regulation of epidermal differentiation.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2014 Feb 1;4(2):a015263. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a015263. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2014. PMID: 24492849 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transgenerational inheritance: how impacts to the epigenetic and genetic information of parents affect offspring health.Hum Reprod Update. 2019 Sep 11;25(5):518-540. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmz017. Hum Reprod Update. 2019. PMID: 31374565
-
Chromatin modulators as facilitating factors in cellular reprogramming.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2013 Oct;23(5):556-61. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2013.07.002. Epub 2013 Aug 28. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2013. PMID: 23993229 Review.
-
Resolving DNA Damage: Epigenetic Regulation of DNA Repair.Molecules. 2020 May 27;25(11):2496. doi: 10.3390/molecules25112496. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32471288 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bioflavonoids promote stable translocations between MLL-AF9 breakpoint cluster regions independent of normal chromosomal context: Model system to screen environmental risks.Environ Mol Mutagen. 2019 Mar;60(2):154-167. doi: 10.1002/em.22245. Epub 2018 Nov 2. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2019. PMID: 30387535 Free PMC article.
-
Bioflavonoids cause DNA double-strand breaks and chromosomal translocations through topoisomerase II-dependent and -independent mechanisms.Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2020 Jan;849:503144. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2020.503144. Epub 2020 Jan 22. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2020. PMID: 32087851 Free PMC article.
-
Rewriting cellular fate: epigenetic interventions in obesity and cellular programming.Mol Med. 2024 Oct 10;30(1):169. doi: 10.1186/s10020-024-00944-2. Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39390356 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Luger K, Mader AW, Richmond RK, Sargent DF, Richmond TJ. Crystal structure of the nucleosome core particle at 2.8 A resolution. Nature. 1997;389:251–60. - PubMed
-
- Luger K, Rechsteiner TJ, Flaus AJ, Waye MM, Richmond TJ. Characterization of nucleosome core particles containing histone proteins made in bacteria. J Mol Biol. 1997;272:301–11. - PubMed
-
- Campos EI, Reinberg D. Histones: annotating chromatin. Annu Rev Genet. 2009;43:559–99. - PubMed
-
- Strahl BD, Allis CD. The language of covalent histone modifications. Nature. 2000;403:41–5. - PubMed
-
- Turner BM. Histone acetylation and an epigenetic code. Bioessays. 2000;22:836–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

