Stable dosages of clobazam for Lennox-Gastaut syndrome are associated with sustained drop-seizure and total-seizure improvements over 3 years
- PMID: 24580023
- PMCID: PMC4303987
- DOI: 10.1111/epi.12561
Stable dosages of clobazam for Lennox-Gastaut syndrome are associated with sustained drop-seizure and total-seizure improvements over 3 years
Abstract
Objective: To determine long-term safety and efficacy of adjunctive clobazam for patients with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome (LGS).
Methods: Eligible patients from two randomized controlled trials (Phase II OV-1002 and Phase III OV-1012) were able to enroll in open-label extension (OLE) study OV-1004 beginning in December 2005 and received clobazam until they discontinued (mandatory at 2 years for patients outside the United States) or until study completion in March 2012. Patients in the United States could have received clobazam for 6 years before it became commercially available. Efficacy assessments included changes in rates of drop seizures and total seizures, responder rates (≥50%, ≥75%, or 100% decreases in seizure frequency vs. baseline), sustained efficacy over time, concomitant antiepileptic drug (AED) use, and global evaluations. Safety assessments included exposure to clobazam, laboratory assessments, physical and neurologic examinations, vital sign monitoring, electrocardiography monitoring, and adverse event reporting.
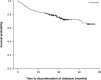
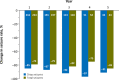
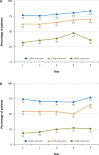
Results: Of 267 patients who enrolled in the OLE, 188 (70%) completed the trial. Two hundred seven patients were from the United States, which was the only country in which patients could be treated with clobazam for >2 years. Forty-four patients were treated with clobazam for 5 years, and 11 for 6 years. Because of the low number of Year 6 patients, this group is not reported separately. Improvements in baseline seizure rates were very stable over the course of the study, with a median 85% decrease in drop seizures at Year 1, 87% at Year 2, 92% at Year 3, 97% at Year 4, and a 91% decrease for patients who had reached Year 5. Similar results were observed for total seizures (79% decrease at both Years 1 and 2, 82% decrease at Year 3, 75% decrease at Year 4, and 85% decrease at Year 5). Responder rates were also stable for the duration of the trial. Of patients who had achieved a ≥50% decrease in median drop-seizure frequency from baseline to Month 3, 86% still had that degree of drop-seizure reduction at Year 3 (and 14% lost their initial responses), and 47% were drop-seizure-free. Most patients who had achieved drop-seizure freedom in the original controlled trials remained drop-seizure-free in the OLE. Based on parents' and physicians' ratings of global evaluations, 80% of patients were "very much improved" or "much improved" after 3 years. Of the 43 patients with concomitant AED data who were treated for 5 years, 30% increased, 19% decreased, and 51% had no change in numbers of AEDs versus their Week 4 regimens. The mean modal clobazam dosage was 0.90 mg/kg/day at Year 1 and 0.97 mg/kg/day at Year 5, suggesting that study patients did not need significant increases in dosage over time. The safety profile was what would be expected for clobazam for LGS patients over a 5-year span, and no new safety concerns developed over time.
Significance: In this largest and longest-running trial in LGS, adjunctive clobazam sustained seizure freedom and substantial seizure improvements at stable dosages through 3 years of therapy in this difficult- to-treat patient population. A PowerPoint slide summarizing this article is available for download in the Supporting Information section here.
Keywords: Antiepileptic drug; Benzodiazepines; Clinical trials; Drop seizures; Epilepsy.
Wiley Periodicals, Inc. © 2014 International League Against Epilepsy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clobazam is efficacious for patients across the spectrum of disease severity of Lennox-Gastaut syndrome: post hoc analyses of clinical trial results by baseline seizure-frequency quartiles and VNS experience.Epilepsy Behav. 2014 Dec;41:47-52. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2014.09.019. Epub 2014 Oct 2. Epilepsy Behav. 2014. PMID: 25282105
-
Randomized, phase III study results of clobazam in Lennox-Gastaut syndrome.Neurology. 2011 Oct 11;77(15):1473-81. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e318232de76. Epub 2011 Sep 28. Neurology. 2011. PMID: 21956725 Clinical Trial.
-
Clobazam : in patients with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome.CNS Drugs. 2012 Nov;26(11):983-91. doi: 10.1007/s40263-012-0007-0. CNS Drugs. 2012. PMID: 23034582 Review.
-
Optimizing clobazam treatment in patients with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome.Epilepsy Behav. 2018 Jan;78:149-154. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2017.10.003. Epub 2017 Dec 22. Epilepsy Behav. 2018. PMID: 29202277
-
Rufinamide: a pharmacoeconomic profile of its use as adjunctive therapy in Lennox-Gastaut syndrome.Pharmacoeconomics. 2012 Mar;30(3):247-56. doi: 10.2165/11208630-000000000-00000. Pharmacoeconomics. 2012. PMID: 22332960 Review.
Cited by
-
Clobazam: A Safe, Efficacious, and Newly Rediscovered Therapeutic for Epilepsy.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2015 Jul;21(7):543-8. doi: 10.1111/cns.12399. Epub 2015 Apr 28. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2015. PMID: 25917225 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Antiseizure Medications on Appetite and Weight in Children.Paediatr Drugs. 2022 Jul;24(4):335-363. doi: 10.1007/s40272-022-00505-2. Epub 2022 May 21. Paediatr Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35596110
-
Expert Opinion on the Management of Lennox-Gastaut Syndrome: Treatment Algorithms and Practical Considerations.Front Neurol. 2017 Sep 29;8:505. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2017.00505. eCollection 2017. Front Neurol. 2017. PMID: 29085326 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perampanel reduces seizure frequency in patients with developmental and epileptic encephalopathy for a long term.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 3;14(1):30051. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-82014-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39627316 Free PMC article.
-
Cannabidiol in patients with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome: Interim analysis of an open-label extension study.Epilepsia. 2019 Mar;60(3):419-428. doi: 10.1111/epi.14670. Epub 2019 Feb 11. Epilepsia. 2019. PMID: 30740695 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Arzimanoglou A, French J, Blume WT, et al. Lennox-Gastaut syndrome: a consensus approach on diagnosis, assessment, management, and trial methodology. Lancet Neurol. 2009;8:82–93. - PubMed
-
- Camfield PR. Definition and natural history of Lennox-Gastaut syndrome. Epilepsia. 2011;52(Suppl. 5):3–9. - PubMed
-
- Chevrie JJ, Aicardi J. Childhood epileptic encephalopathy with slow spike-wave. A statistical study of 80 cases. Epilepsia. 1972;13:259–271. - PubMed
-
- Berg AT, Shinnar S, Testa FM, et al. Mortality in childhood-onset epilepsy. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2004;158:1147–1152. - PubMed
-
- Crumrine PK. Lennox-Gastaut syndrome. J Child Neurol. 2002;17(Suppl. 1):S70–S75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

