Akt inhibitor MK-2206 promotes anti-tumor activity and cell death by modulation of AIF and Ezrin in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 24581231
- PMCID: PMC3941258
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-145
Akt inhibitor MK-2206 promotes anti-tumor activity and cell death by modulation of AIF and Ezrin in colorectal cancer
Abstract
Background: There is extensive evidence for the role of aberrant cell survival signaling mechanisms in cancer progression and metastasis. Akt is a major component of cell survival-signaling mechanisms in several types of cancer. It has been shown that activated Akt stabilizes XIAP by S87 phosphorylation leading to survivin/XIAP complex formation, caspase inhibition and cytoprotection of cancer cells. We have reported that TGFβ/PKA/PP2A-mediated tumor suppressor signaling regulates Akt phosphorylation in association with the dissociation of survivin/XIAP complexes leading to inhibition of stress-dependent induction of cell survival.
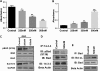
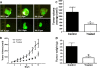
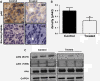
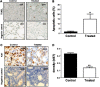
Methods: IGF1R-dependent colon cancer cells (GEO and CBS) were used for the study. Effects on cell proliferation and cell death were determined in the presence of MK-2206. Xenograft studies were performed to determine the effect of MK-2206 on tumor volume. The effect on various cell death markers such as XIAP, survivin, AIF, Ezrin, pEzrin was determined by western blot analysis. Graph pad 5.0 was used for statistical analysis. P < 0.05 was considered significant.
Results: We characterized the mechanisms by which a novel Akt kinase inhibitor MK-2206 induced cell death in IGF1R-dependent colorectal cancer (CRC) cells with upregulated PI3K/Akt signaling in response to IGF1R activation. MK-2206 treatment generated a significant reduction in tumor growth in vivo and promoted cell death through two mechanisms. This is the first report demonstrating that Akt inactivation by MK-2206 leads to induction of and mitochondria-to-nuclear localization of the Apoptosis Inducing Factor (AIF), which is involved in caspase-independent cell death. We also observed that exposure to MK-2206 dephosphorylated Ezrin at the T567 site leading to the disruption of Akt-pEzrin-XIAP cell survival signaling. Ezrin phosphorylation at this site has been associated with malignant progression in solid tumors.
Conclusion: The identification of these 2 novel mechanisms leading to induction of cell death indicates MK-2206 might be a potential clinical candidate for therapeutic targeting of the subset of IGF1R-dependent cancers in CRC.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ezrin expression and cell survival regulation in colorectal cancer.Cell Signal. 2014 May;26(5):868-79. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.01.014. Epub 2014 Jan 22. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24462708 Free PMC article.
-
TGFβ and IGF1R signaling activates protein kinase A through differential regulation of ezrin phosphorylation in colon cancer cells.J Biol Chem. 2018 May 25;293(21):8242-8254. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.001299. Epub 2018 Mar 29. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29599290 Free PMC article.
-
Selective AKT Inhibition by MK-2206 Represses Colorectal Cancer-Initiating Stem Cells.Ann Surg Oncol. 2016 Sep;23(9):2849-57. doi: 10.1245/s10434-016-5218-z. Epub 2016 Apr 8. Ann Surg Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27059026 Free PMC article.
-
Cell survival and metastasis regulation by Akt signaling in colorectal cancer.Cell Signal. 2013 Aug;25(8):1711-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.03.025. Epub 2013 Apr 18. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23603750 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Mini Review on Molecules Inducing Caspase-Independent Cell Death: A New Route to Cancer Therapy.Molecules. 2022 Sep 28;27(19):6401. doi: 10.3390/molecules27196401. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36234938 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic and therapeutic implications of NHERF1 expression and regulation in colorectal cancer.J Surg Oncol. 2020 Mar;121(3):547-560. doi: 10.1002/jso.25805. Epub 2019 Dec 22. J Surg Oncol. 2020. PMID: 31867736 Free PMC article.
-
Pathophysiological mechanisms of death resistance in colorectal carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Nov 7;21(41):11777-92. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i41.11777. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26557002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of posttranslational modifications in lipid metabolism and cancer progression.Biomark Res. 2024 Nov 18;12(1):141. doi: 10.1186/s40364-024-00681-y. Biomark Res. 2024. PMID: 39551780 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Importance of Survivin in Stem Cells and Cancer: the Development of New Cancer Therapeutics.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2020 Oct;16(5):828-852. doi: 10.1007/s12015-020-09995-4. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2020. PMID: 32691369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ubiquitin-specific peptidase 17 promotes cisplatin resistance via PI3K/AKT activation in non-small cell lung cancer.Oncol Lett. 2020 Jul;20(1):67-74. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.11568. Epub 2020 Apr 23. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32565935 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grabinski N, Bartkowiak K, Grupp K, Brandt B, Pantel K, Jucker M. Distinct functional roles of Akt isoforms for proliferation, survival, migration and EGF-mediated signalling in lung cancer derived disseminated tumor cells. Cell Signal. 2011;23(12):1952–1960. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2011.07.003. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fayard E, Xue G, Parcellier A, Bozulic L, Hemmings BA. Protein kinase B (PKB/Akt), a key mediator of the PI3K signaling pathway. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2011;346:31–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

