Hippo signaling regulates microprocessor and links cell-density-dependent miRNA biogenesis to cancer
- PMID: 24581491
- PMCID: PMC3982296
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.12.043
Hippo signaling regulates microprocessor and links cell-density-dependent miRNA biogenesis to cancer
Abstract
Global downregulation of microRNAs (miRNAs) is commonly observed in human cancers and can have a causative role in tumorigenesis. The mechanisms responsible for this phenomenon remain poorly understood. Here, we show that YAP, the downstream target of the tumor-suppressive Hippo-signaling pathway regulates miRNA biogenesis in a cell-density-dependent manner. At low cell density, nuclear YAP binds and sequesters p72 (DDX17), a regulatory component of the miRNA-processing machinery. At high cell density, Hippo-mediated cytoplasmic retention of YAP facilitates p72 association with Microprocessor and binding to a specific sequence motif in pri-miRNAs. Inactivation of the Hippo pathway or expression of constitutively active YAP causes widespread miRNA suppression in cells and tumors and a corresponding posttranscriptional induction of MYC expression. Thus, the Hippo pathway links contact-inhibition regulation to miRNA biogenesis and may be responsible for the widespread miRNA repression observed in cancer.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
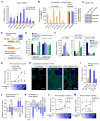
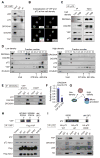
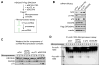
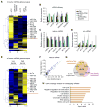
Comment in
-
Tumour suppressors: Hippo promotes microRNA processing.Nat Rev Cancer. 2014 Apr;14(4):216-7. doi: 10.1038/nrc3715. Nat Rev Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24658271 No abstract available.
References
-
- Camargo FD, Gokhale S, Johnnidis JB, Fu D, Bell GW, Jaenisch R, Brummelkamp TR. YAP1 increases organ size and expands undifferentiated progenitor cells. Curr Biol. 2007;17:2054–2060. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

